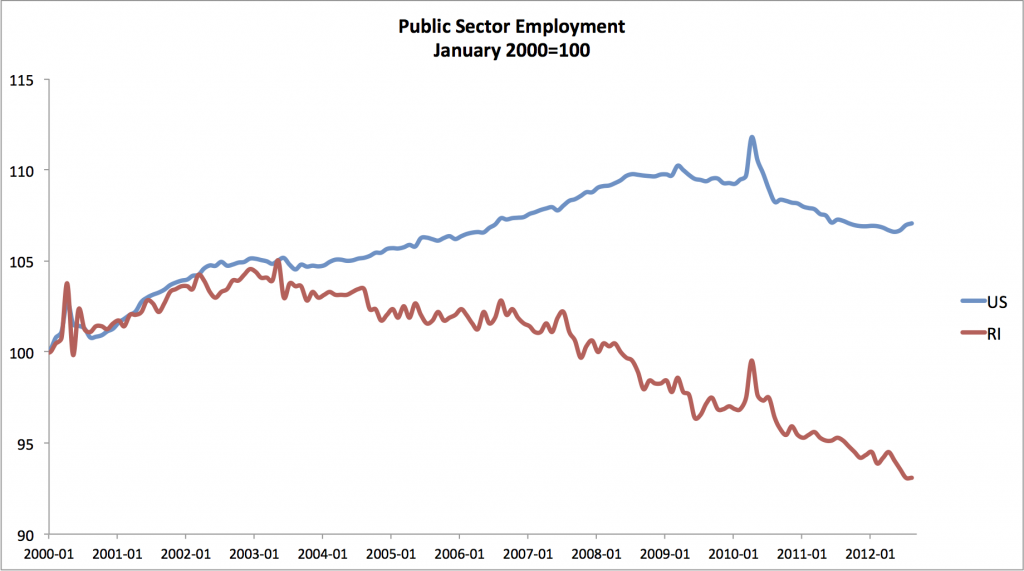
I ended my previous post on a promise to dig into the mechanics of how Carcieri orchestrated the downfall of the Rhode Island economy. Naturally, we begin with something Carcieri took great pride in—laying off huge numbers of public sector workers. To show just how severe the public sector cutbacks were under Carcieri, I’ve plotted the Ocean State’s public sector workforce alongside the national numbers since 2000. (Both are normalized to 100 at January 2000.)
Before Carcieri’s cuts began to bite, Rhode Island public employment tracked the national numbers fairly closely, but once his policies were in place, Rhode Island’s public sector decoupled from the national public sector and took a precipitous nosedive. The bleeding has continued ever since. The pace of the widening of the gap accelerated in late 2006 after the passage of the 2006 budget, with its infamous tax cuts for the rich, but things didn’t end there. Even though public employment began falling all around the country in the aftermath of the recession, we still lost 7.75% of state and local public sector employees between January of 2008 and April of 2012—the second highest drop in the nation.
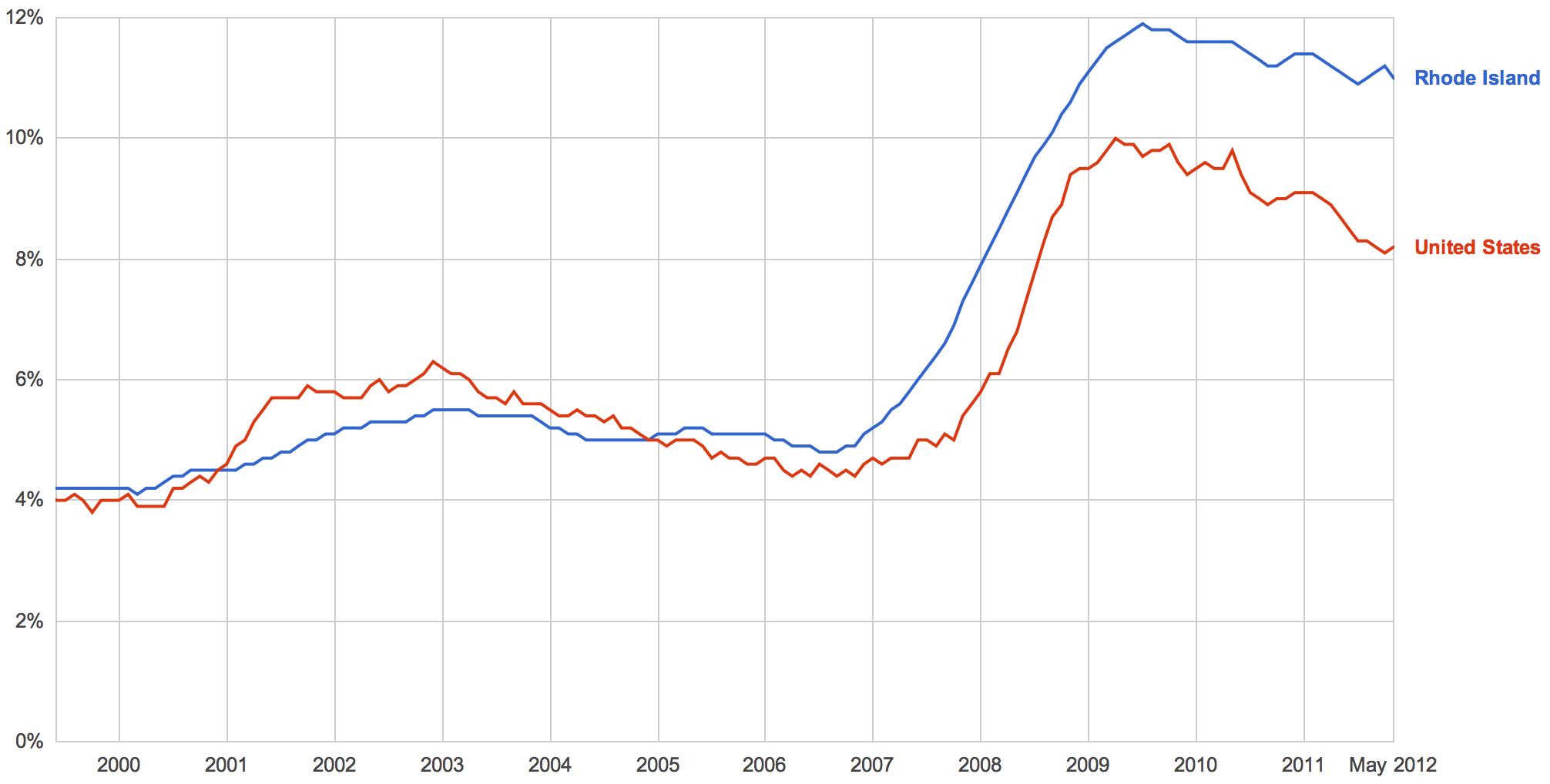
In conservative junk economics, laying off those greedy public sector workers is always a great idea, but of course, in the real world those layoffs can have devastating effects on the economy. To begin with, the jobs lost in the public sector are themselves jobs the Rhode Island economy has lost. If public employment in Rhode Island had followed the same trajectory as it did in the nation since 2000, we would have almost 9,000 more jobs in the public sector than we do now, and the unemployment rate would be 1.6 percentage points lower. Roughly half of our unemployment gap is the direct result of mass layoffs in the public sector.
The devastation caused by public sector layoffs does not end there. When public workers are laid off, their finances are devastated, and they start spending much less, driving down the demand for goods and services in Rhode Island. They also don’t have the money to buy new houses and can often wind up in foreclosure, which has devastating effects on the housing market. Rhode Island also ceases to benefit from the work that the public sector workers used to do. As Scott MacKay notes, Carcieri oversaw a general breakdown of government services that Chafee has spent much of his term in office trying to clean up.
Everyone has their favorite story of mistreatment at the hands of our government, but mine is the angry letter I received accusing me of not paying my state income tax. When I called up to protest that Rhode Island had already removed the money from my bank account, the woman I finally reached explained to me that they didn’t really have the staff to check whether everyone they were sending these letters to actually hadn’t paid their taxes.
Estimating the magnitude of the collateral damage from Rhode Island’s public sector mass layoffs is difficult, but it is probably fair to say that does not explain all of the rest of the unemployment gap between Rhode Island and the U.S. average. Part of the rest comes from other public sector cuts, many of which were far more savage than the national average. Pensions cuts, stagnant wages, and reduced morale most likely took their toll by reducing demand, but these cuts happened in other states as well, and much of the pain is spread out over several decades, so it remains unclear how much they added to our unemployment gap (probably no more than a few tenths of a percentage point).
Although the Rhode Island media are reluctant to use the word, what happened in Rhode Island was basically European-style austerity. When governments decide to throw out a century of economics and pretend that taking a chainsaw to the public sector will somehow magically not wreck the economy, the results aren’t pretty. This is partially because serious austerity measures like Carcieri’s public sector cuts can lock an economy into the austerity death spiral, where austerity weakens the economy, prompting more austerity. This is a lesson being learned not just in Europe, but also in states like Rhode Island that went all in for the same bad economic policies. All across America, the states that opted for austerity during the recession performed worse than states that did not. When conservative extremist Scott Walker took over in Wisconsin and implemented a severe austerity package that prompted mass protests, Wisconsin’s unemployment rate exploded. A similar wave of job losses is currently blowing through the Northeast region as governments from Maine to Pennsylvania opt for mass layoffs. Because Rhode Island’s recent public sector layoffs have been more in line with the national average, we have largely escaped this regional recession.
Comparing us with the broader Northeast region, however, does not usually paint Rhode Island’s economy in a very flattering light. In fact, because most of the Northeast region did not do as badly as the rest of the country, Rhode Island’s singularly bad record is even worse than it looks. So while public sector cuts explain most of our unemployment gap, alone they do not explain all of it. Some other factor must be at work here, a factor that will be the subject of tomorrow’s post.