In past posts, I have explained actions that businesses–usually large corporations–have taken that are decidedly contrary to the interests of the general public. For this, commentors have claimed that I’m anti-business, that I’m using scare tactics, I’m just a socialist, or some combination thereof.
In past posts, I have explained actions that businesses–usually large corporations–have taken that are decidedly contrary to the interests of the general public. For this, commentors have claimed that I’m anti-business, that I’m using scare tactics, I’m just a socialist, or some combination thereof.
However, in the news over the past month or so we have seen two excellent examples of Business Behaving Badly. The first, of course, was the decision of MetLife to summarily fire all of its Life Administration employees here in RI and other parts of the Northeast and across the country, in order to move those jobs to North Carolina. MetLife is firing these people in order to pad its already high profits: $1.4 Bn for 2012. That seems to be contrary to the interests of the general public.
And yes, these people are being fired. There is no other word that accurately describes what is happening. Fired. For no fault of their own. Without cause. With no justification other than it better suits Met’s interests. A lot of these people have worked loyally for Met for periods often measured in decades. The reward for loyal service is to be fired.
How does that fit with the propaganda that the free market will take care of employees better than any government? Answer, it doesn’t. What it does do is illustrate to perfection how a corporation will take care of its own needs, regardless of the number of lives that are damaged in the process. It’s all about increasing the benefits that flow in a torrent to those already at the apex of the financial pyramid.
The second example is the explosion of the fertilizer plant in West, Texas. Now, from what I can gather, this plant was not part of some multinational corporation. A company like Met could have bought and sold it out of the spare change in the couch cushions. But it was a business, run for profit. One way of increasing profit is to cut corners on safety issues. Despite the fact that ammonium nitrate was the explosive of choice used by Timothy McVeigh in the Oklahoma City bombing, those in charge of the fertilizer plant did not consider this a safety risk, Records indicate that the risk that concerned them most was the possibility of a leak of ammonia gas. This would be a bad thing, but not catastrophic.
So the company took no steps to mitigate the possible risk. Why not? Because they did not see the need, and taking steps would have cost money.
Now, it appears that no one in the town particularly blames the company, and the company was certainly not a rapacious corporation hell-bent on increasing profit. Still, the fact remains that no safety precautions were taken, and fifteen people are dead because of the lack of precautions.
The third example is the worst and most blatant of all: the collapse of the building in Bangladesh.
One thing we all hear about is the need for ‘common sense’. Doesn’t it seem that ‘common sense’ should include taking precautions to reduce the risk of a fire at a plant that stores large quantities of highly-explosive material? If you’re making dynamite, shouldn’t you build risk-mitigation into your plans? And ammonium nitrate, in the quantities on hand at the fertilizer plant is every bit as dangerous as dynamite. You can take Timothy McVeigh’s word on that. Doesn’t ‘common sense’ tell you to build a building so it won’t collapse?
It also appears that the fertilizer company may not have actually broken any laws. That also seems to be part of the problem. The plant is in Texas, and Texas prides itself on being a land of lax regulation. So fifteen people died so Texas could maintain its macho image of ‘hands-off’ conservatism. IOW, it’s more like Bangladesh, and less like the rest of the US that foolishly insists on standards. More, 68 people have died in mining accidents in the new millennium. The common thread of all these deaths is the lack of safety precautions. Why did the companies in question not take proper precautions? Because they cost money, and no one made them take the precautions.
In many ways, the impression is that the West Fertilizer Company was actually a fairly benign employer. In many ways, that only makes things worse. If this is how a well-intentioned company acts, how much worse are those actively looking for corners to cut?
This is how business will operate in an unregulated, or lightly-regulated market. Most businesses will be responsible, but there will always be a few who don’t. And when these businesses behave irresponsibly, and profit from this lack of concern, others will mimic that behavior and start cutting corners, too. And people will die. And it doesn’t have to be a business like mining, or fertilizer production with their built-in dangers; it could be the result of locked or nonexistent emergency exits, as happened in the Hamlet, NC chicken plant fire where 25 people died, or the even more horrific Triangle Shirtwaist fire, which killed over 140 people.
We are told that regulations in the US are too onerous. That they cost businesses money, and so jobs. We are told we need to lighten the regulatory burden on business, so that we can create jobs. IOW, we need to become more like Bangladesh, with its light (non-existent? Certainly not-enforced) regulations, no unions, and starvation wages for its employees.
You get what you pay for.
This is what happens when businesses are left to police themselves. Things are no different now than they were a century ago.
]]>
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 2448
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
I too start with questions: “What would cause us, upstanding seniors, to stand on street corners, dressed like fools, singing songs with our own, supposedly epoch-making Raging Granny lyrics? And, you who know what we know, what are you doing?”

Raging Grannies protesting. (Photo by Danielle Dirocco)
What, in fact, do I know that deeply concerns my inner scientist-grandfather? As Hansen explains, greenhouse gasses cover the Earth with a blanket that makes it absorb more solar power than it radiates back into space. To restore the energy balance, the Earth heats up as required by laws of physics, laws soon to be repealed by an ALEC inspired legislature near you.
Let Hansen speak:
The total energy imbalance now is about six-tenths of a watt per square meter. That may not sound like much, but when added up over the whole world, it’s enormous. It’s about 20 times greater than the rate of energy use by all of humanity. It’s equivalent to exploding 400,000 Hiroshima atomic bombs per day 365 days per year. That’s how much extra energy Earth is gaining each day. This imbalance, if we want to stabilize climate, means that we must reduce CO2 from 391 ppm, parts per million, back to 350 ppm. That is the change needed to restore energy balance and prevent further warming.
Those of us who are not addicted to this so-last-century medium called TV know the problems caused by global warming, but not all may realize the magnitude and frequency of the extremes that have ravaged the Earth during the last decades. Yes, we have seen the heat waves, the droughts, the wild fires, and the record breaking hurricanes and typhoons. But nothing is more variable than the weather! So, why should we be worried by a list like this? Indeed, no particular item is anything new under the Sun, but new is the frequency of extreme weather events. Hansen and coworkers[1] did the statistics and found —emphasis mine— that:
An important change is the emergence of a category of summertime extremely hot outliers, more than three standard deviations (3σ) warmer than the climatology of the 1951-1980 base period. This hot extreme, which covered much less than 1% of Earth’s surface during the base period, now typically covers about 10% of the land area. It follows that we can state, with a high degree of confidence, that extreme anomalies such as those in Texas and Oklahoma in 2011 and Moscow in 2010 were a consequence of global warming because their likelihood in the absence of global warming was exceedingly small. We discuss practical implications of this substantial, growing, climate change.
How does the focus-group driven world of denial, aka American politics, respond to this string of disasters? In an interview with Jessica Sites of In These Times indefatigable Amy Goodman of Democracy Now!’ comments:
We are the ones making that connection; the corporate media does not. In all three debates between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, do you know how many times the words ‘climate change’ came up? None.
Am I the only one who thinks that these so-called leaders should be tried for complicity in a conspiracy to commit genocide? It seems that to those of us who do not have their brains washed by the Supreme Courtisans of the Corporate States of America this should be a clear a case:
Article II of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide: “(c) Deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part;”
“Group” here refers to that half of humanity who cannot afford privatized, distilled water, and filtered, cold air, to be sold by the Corporations of Mass Destruction that own government.
Oh well, those ElecToon debates took place before we won the elections, which, as we all know, ended in a mandate for change, as they always do. Yet, somehow, we are wasting time on inane fiscal cliff theatrics. Why? To further the bipartisan program of shredding the social contract by unbridled privatization and imperial overreach, brought to us by the “world’s best military.” Indeed, as Major Ralph Peters describes it: “The de facto role of the US armed forces will be to keep the world safe for our economy and open to our cultural assault. To those ends, we will do a fair amount of killing.”
Chief Sitting Bull (Tatanka Iyotake) diagnoses this sick conduct of the “developed” world like this:
Strangely enough, they have a mind to till the soil, and the love of possessions is a disease in them. These people have made many rules that the rich may break, but the poor may not! They have a religion in which the poor worship, but the rich will not! They even take tithes of the poor and weak to support the rich and those who rule. They claim this mother of ours, the Earth, for their own use, and fence their neighbors away from her, and deface her with their buildings and their refuse. They compel her to produce out of season, and when sterile she is made to take medicine in order to produce again. All this is sacrilege.
You can find this quote in Days of Destruction Days of Revolt, Chris Hedges’ and Joe Sacco’s agonizing account of their travels in “sacrifice zones,” those areas ruined in the name of unbridled profit, progress, and industrial advancement. This exchange between
Chris Hedges and Bill Moyers sums it up perfectly:
CHRIS HEDGES: There’s no way to control corporate power. The system has broken down, whether it’s Democrat or Republican. And because of that, we’ve all become commodities. Just as the natural world has become a commodity that is being exploited until it is exhausted, or it collapses.
BILL MOYERS: You call them sacrifice zones.
CHRIS HEDGES: Right.
BILL MOYERS: Explain what you mean by that.
CHRIS HEDGES: Well, they have the individuals who live within those areas have no power. The political system is bought off, the judicial system is bought off, the law enforcement system services the interests of power, they have been rendered powerless. You see that in the coal fields of Southern West Virginia.
[…]
And when we flew over the Appalachians, and it’s a terrifying experience, because you realize only then do you realize how vast the devastation is. Just as when we were both in the war in Bosnia, you couldn’t grasp the destruction of ethnic cleansing until you actually flew over Bosnia, and village after village after village had been razed and destroyed.And the same was true in the Appalachian Mountains. And these people are poisoned. The water is poisoned, it smells, the soil is poisoned. And the people who are making tremendous profits from this don’t even live in West Virginia—
Of course, the World according to Peabody Coal Company and Bechtel Corporation, assisted by their flunkies of government by and for the Ruling Class was documented in Broken Rainbow(1985). Libraries have been filled with accounts of our colonial exploits. Indeed, in 1860 the Dutch writer known by his pen name Multatuli wrote about the former Dutch colonial sacrifice zone, today’s Indonesia, and lamented: “I told you, reader, that my story is monotonous.” Therefore, let us sing Songs of Rage by Grannies Marlies and Paige, and the Raging Grannies of Greater Westerly:
Miner’s Lament
(Tune of My Darling Clementine)
In the cabins
In the canyons
Live our families on the dole
They have asthma
They have cancer
And the wind blows black as coalOh my homeland
Oh my homeland
Oh my Blue Ridge Mountain home
Once I was a simple miner
Now the mountain tops are goneWith the treasures
In our valleys
We should all be millionaires
Corporations took our profits
Left the landscape scarred and bareOh my homeland
Oh my homeland
Oh my Blue Ridge Mountain home
You are lost and gone forever
And the mountain tops are blown
(right off!)
Fiscal Cliff Talk
(Tune of Little Boxes)
Fiscal cliff talk as the globe warms,
Fiscal cliff talk as they dilly dally,
Fiscal cliff talk on the bube tube,
Fiscal cliff talk is a scam.
There’s the wild fires and the dust bowl,
And the heat waves and the hurricanes,
And the pols seem but to dilly dally,
And they all want just the same.Fiscal cliff talk on the bube tube,
Fiscal cliff talk but to dilly dally,
Fiscal cliff talk, fiscal cliff talk,
Fiscal cliff talk is a scam.
There’s the Blue Dogs and the Red Dogs,
And the Dem talk and the Repub talk,
And they all seem but to dilly dally,
And they all want just the same.See the people on the bube tube
Carry water for the ruling class,
Medicare cuts, Medicaid cuts,
Payoffs for gigantic greed.
And there’s home loans and there’s student loans,
And the debt collectors agencies,
‘Cuz the rich need their entitlements.
Let the common good be damned!With austerity and with deep cuts,
They shall tear up social safety nets.
For all drama ’bout posterity,
Fiscal cliff talk is a scam.
With their pipelines and their tar sands,
They will sell off the environment,
But they don’t care ’bout posterity,
As they buy and sell the Earth.
1. Hansen, J., Mki. Sato, and R. Ruedy, 2012: Perception of climate change, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 109, 14726-14727, E2415-E2423, doi:10.1073/pnas.1205276109.
![]()

- Introduction: The Carcieri Effect
- Part 2: Austerity’e Effects
- Part 3: Tax Cuts for the Affluent
- Part 4: Property Tax Hikes
- Part 5: Unemployment Insurance Taxes
- Part 6: Competitiveness
- Conclusion: Have We Learned Our Lesson?
Governor Carcieri did not have to launch a jihad against public sector employment. Nor was it necessary to hand massive tax breaks to the wealthy. Had we avoided those tax breaks, we wouldn’t have had to slash municipal aid and send property taxes through the roof. Had we not raised property taxes, we would have a stronger housing market, and had we not engaged in massive austerity, the rest of our economy would be doing better as well. If our unemployment insurance tax rate were less punitive, then fewer businesses would have gone under. None of this had to happen.
It seems that things are finally looking up for the Rhode Island economy. Unemployment is falling, despite a regional recession, and numerous other economic indicators are showing positive signs.
There remain many road blocks ahead for our economy, as we deal with the aftermath of 38 Studios, municipal budget disasters, and other legacies of the Carcieri era, so it is by no means clear that these positive trends will continue, but there is certainly more cause for optimism now than we have had for quite some time.
As Leonard Lardaro, an economist at URI, puts it, we’re “in a recovery the magnitude of which almost nobody in this state seems to fully comprehend.” But we should not take this as evidence that the economy of the Ocean State is suddenly being managed well. Rhode Island is a severely depressed economy with relatively strong fundamentals. If you don’t keep kicking it, it will recover, even if the transition is only from terrible to mediocre leadership.
Carcieri is gone, it is true. But the very conservative General Assembly was fully complicit in Carcieri’s blunders, earning them effusive praise from the Wall St. Journal. As Dan Lawlor puts it, “it is remarkable how much of his vision was enacted, sometimes excitedly, by the Democratic General Assembly and its leaders, specifically Gordon Fox and Theresa Paiva Weed.”
There is much truth to this. Although it is hard to argue that pro-choice, pro-marriage Fox isn’t at least a moderate improvement over his predecessors, as House Majority Leader, he was a major proponent of the income tax cuts at the heart of Rhode Island’s problems.
After a bruising reelection battle, Fox made mild noises about potentially being more open to sensible tax reform, but given his past record, it is unclear whether anything will come of this. Nominally a Democrat, Paiva Weed shares Fox’s rather extreme economic conservatism, but she does not share Fox’s more moderate social views. Indeed, she is probably the primary obstacle to marriage equality passing in 2013.
Although Chafee is pushing for some distinctly insufficient reforms, they will probably mostly fail, and it is hard to imagine the General Assembly putting together anything remotely up to the task.
What must be done is actually quite straightforward. We need a jobs bill and tax reform: We need to reverse Carcieri’s austerity by rehiring the teachers, firefighters, and policemen whose jobs he cut. We should also make new investments in critical areas, restoring our crumbling roads and bridges, creating bicycle infrastructure and commuter rail lines, expanding and improving URI, and building tons of medical schools to take advantage of the extreme demand for new doctors. We should begin paring back property taxes and fixing budgets by restoring aid to cities and towns and allowing them to levy local income taxes to offset property taxes.
To pay for all this, we should restore the pre-2006 income tax rates and create new brackets for the wealthy, with a top marginal rate of at least 13%. We also need to restructure the hugely regressive unemployment insurance tax as a simple and constant flat, low rate, a reform that could easily raise revenue while making the tax code much less regressive and much more business-friendly.
With the current conservatives in office, almost none of this will happen. But it is definitely worth fighting for.
]]>
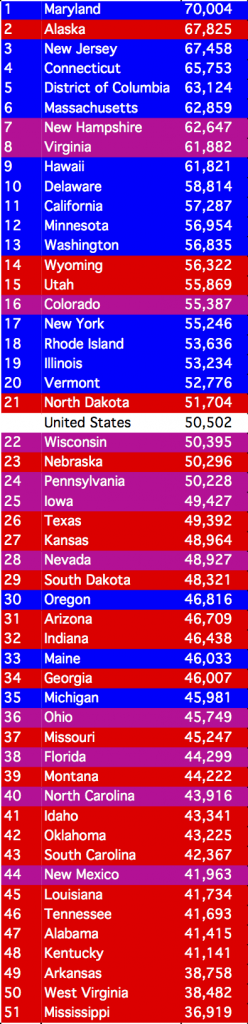
What I am referring to is actual competitiveness. Although the Ocean State GOP would have you think otherwise, Rhode Island is not the poorest state in the union. Actually, we rank a bit above the average. The issue is that we are much poorer than the other blue states that surround us, as the rankings of states by median household income show.
As a blue state with a long history of unusually conservative government, this is to be expected. It does, however, have some consequences for our economy. By being a moderately wealthy state surrounded by much more successful states, we get many of the disadvantages of affluence with few of its benefits. One way this manifests itself is the strength of our currency. Because the Northeast is a wealthy region, it has a strong dollar, but this is more of a regional trend than a state-based one. A strong currency makes it harder for a state to compete in trade, which is why we want the Chinese to let their currency strengthen. This probably results in a trade deficit for Rhode Island, but the government does not track the trade positions of individual states, so it is impossible to know for sure. At the same time, we also suffer from competition with wealthier neighboring states, which can offer both lower taxes and better government services because of their wealth, as Josh Barro points out in Forbes. Competition probably explains a small portion of our unemployment gap, but the bulk of the blame falls on massive austerity and unusually silly tax polices.
High unemployment insurance taxes can help exacerbate an economic collapse because once a business is forced to make layoffs, its tax rate can skyrocket. This tends to help push struggling businesses over the line, and Rhode Island’s high unemployment insurance tax rate pushed us over the line. In the Tax Foundation’s 2013 Business Tax Climate Index, the gold standard for biased conservative tax climate rankings, the unemployment insurance tax is the only tax category where Rhode Island ranks last. There is relatively little evidence that a better tax climate ranking helps a state become more competitive, but there are real competitiveness issues that do matter, and they are the subject of tomorrow’s column.
]]>A critical mechanism for financing the income tax cuts for the rich was slashing the aid that the state government sends to the cities and towns. These severe cuts resulted in a wave of municipal budget crises that we are all too familiar with. Cities and towns closed part of the gap through severe cuts, but they also responded with drastic property tax hikes. Property taxes are notorious for being unusually bad for the economy. Even the Tax Foundation, a very conservative think tank, agrees that property taxes have a bigger effect on business location decisions than any of the other major taxes. Simply put, property tax hikes are very hard on business. The pain is not distributed evenly; property taxes hit small businesses especially hard. The problem is especially severe because the aid cuts were worst in Providence and Woonsocket, where businesses are disproportionately located, so the property tax hikes were worst in areas with the most businesses.
The other side of the economic devastation wrought by property taxes is the property tax on families, which squeezes budgets hard and reduces demand. Because the middle class is more likely to spend its money in ways that are good for the overall economy, shifting the tax budget to the middle class is a big blow to the economy. Redistributing wealth from the middle class to the rich is an especially bad idea when the vehicle is property taxes, because higher property taxes do extensive collateral damage. In the long term, property taxes create perverse incentives that lead to bad urban planning, extensive sprawl, and economic segregation of schools, but they also do serious damage to the housing market. The primary cause of the second Bush recession was the bursting of the housing bubble that inflated during most of Bush’s term in office. Like every state in the union, Rhode Island saw its housing market collapse. This was not the time to raise property tax rates sky high.
In much the same way as austerity begets more austerity by crashing the economy, property tax hikes can lock an economy into a vicious cycle, where higher property taxes depress the housing market, which in turn reduces revenue and requires higher property tax rates. States with large property tax burdens are particularly vulnerable to this feedback loop. Rhode Island, of course, is one of those states with large property tax burdens. Here’s how our tax revenue breaks down by the kind of tax:
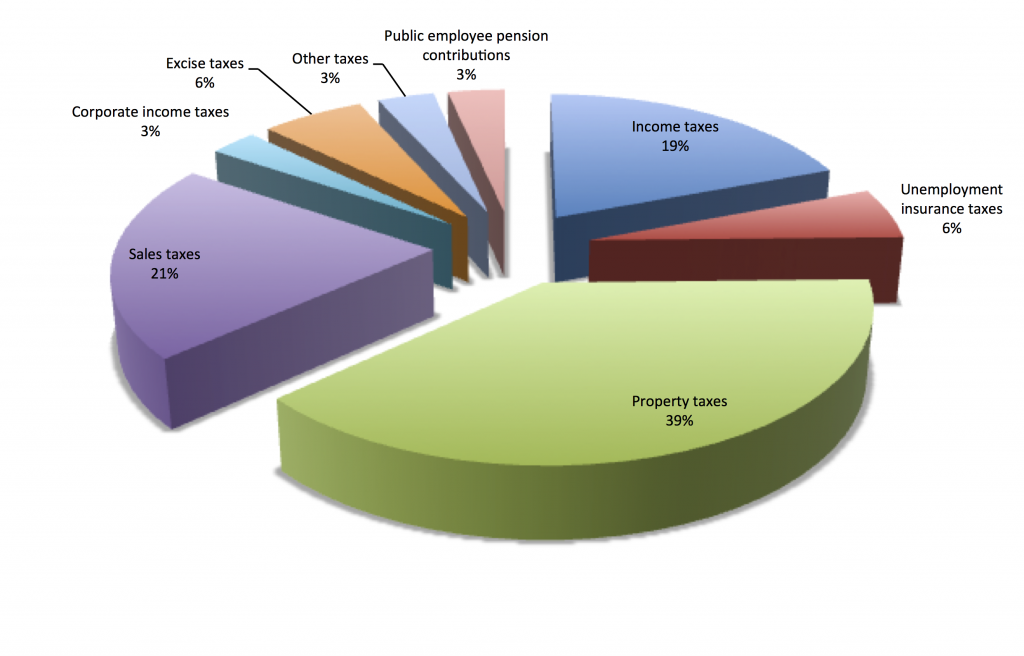
- Breakdown of Rhode Island tax revenue by type. Data from www.usgovernmentrevenue.com.
One of the consequences of our high property taxes is that our tax system is even worse than usual about taxing the 99% at a higher rate than the 1%. In Rhode Island, the bottom 20% pay a rate of 11.9%, and the top 1% pay a rate of only 5.6%. You can see how the burden breaks down in this (slightly out of date) graph from the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy’s “Who Pays?” report. (For a fuller discussion of how this works, see Ted Nesi’s excellent piece in Providence Business News.)
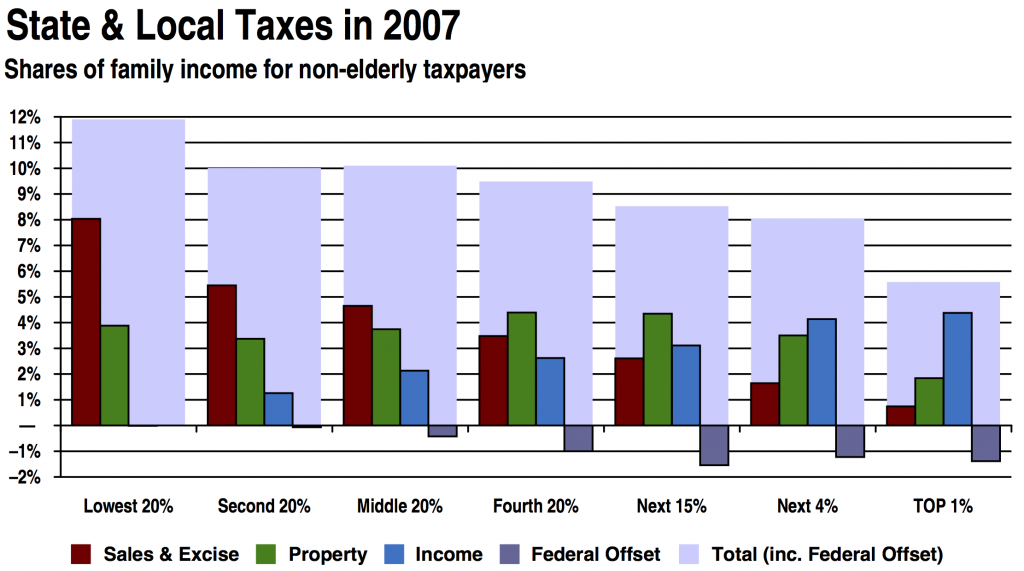
- Tax distribution in Rhode Island broken down by the Institute for Taxation and Economic Policy. This study was done on 2007 rates but updated for changes to the tax code up to 2009.
]]>
As I noted in the first column, the bottom fell out of the Rhode Island economy in late 2007, nearly a year before the second Bush recession began. Perhaps it is just a curious coincidence that this happened as the effect of the income tax cuts for the wealthy passed in 2006 began to kick in, but I suspect not. Indeed, there is considerable evidence that it was these tax cuts that triggered the collapse of our economy.
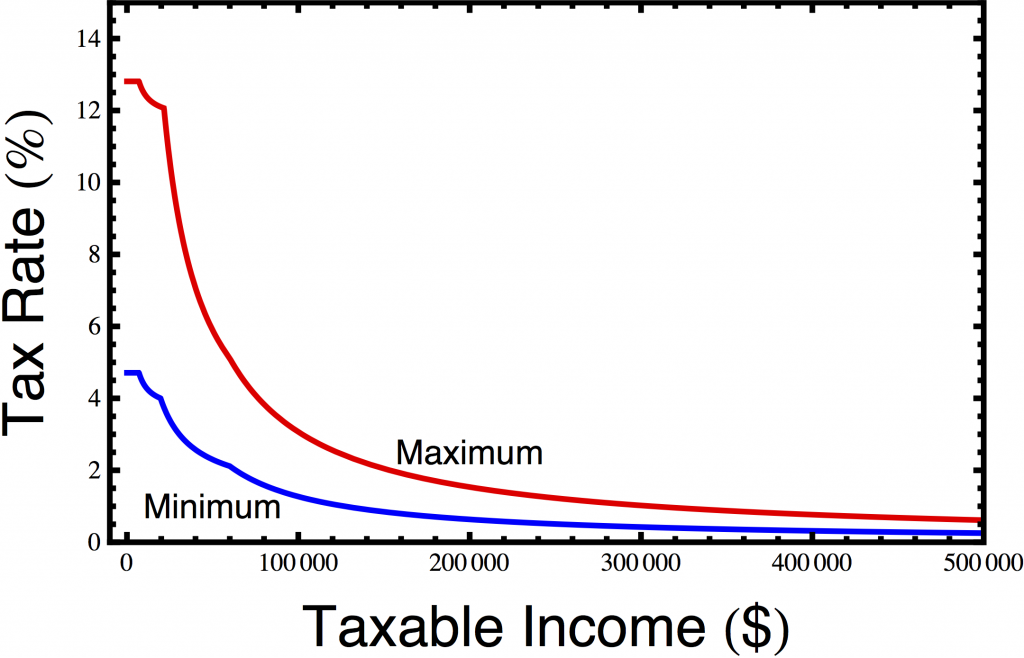
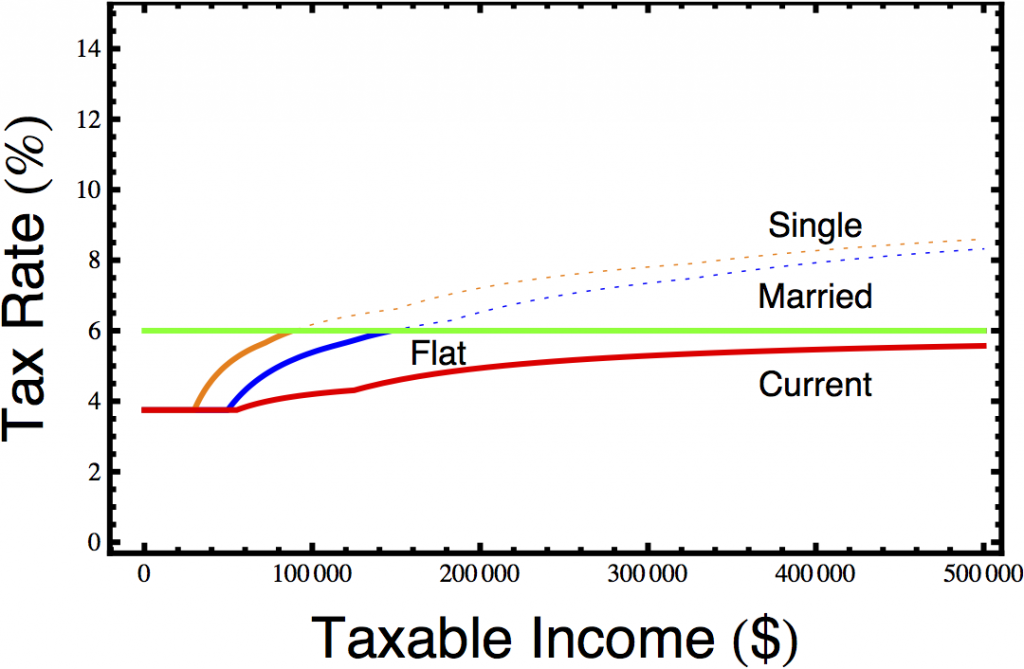
The details of the tax cuts are slightly complicated. The original tax cut passed in 2006 and imposed an alternate flat tax rate that you could choose to pay instead of the traditional tax brackets. This rate started at 8% and fell by 0.5 percentage per year, hitting 6% in 2010, but in 2010, the government overhauled the tax code again in a tax cut aimed primarily at the upper middle class. You can see the three different rate schemes in the graph below.
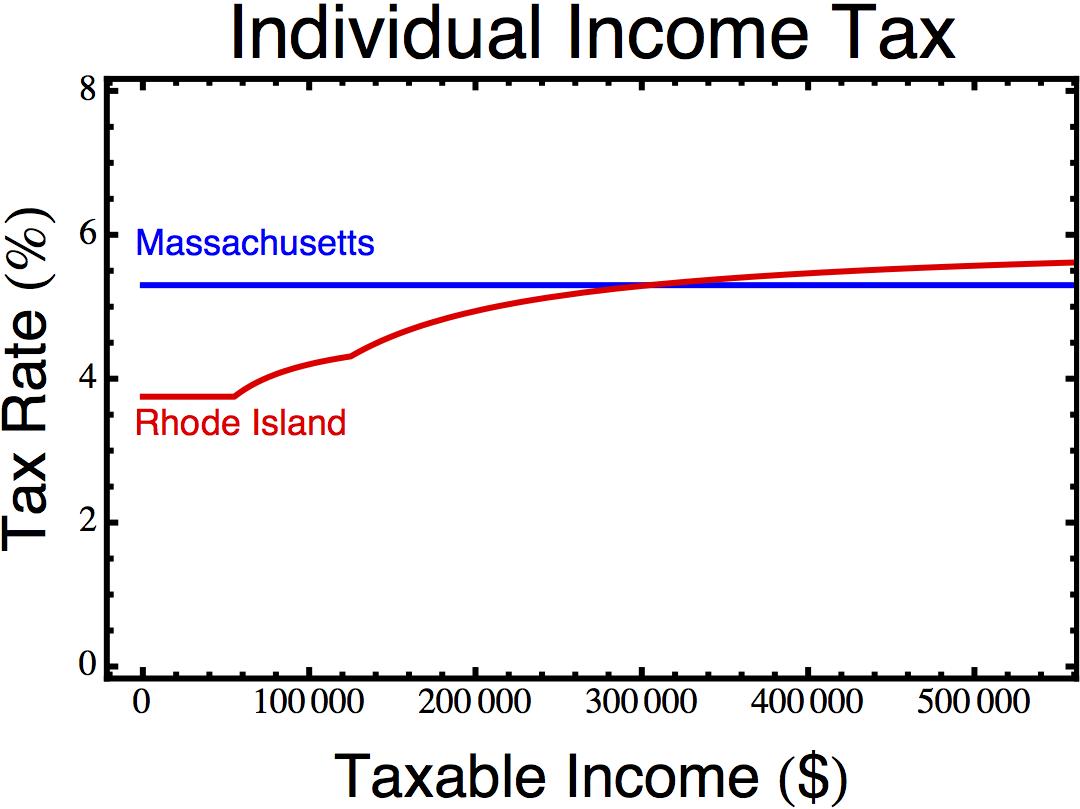
Perhaps the most troubling aspect of these tax cuts is that they were pushed largely by Democrats, an act of conservatism that elated the Wall St. Journal’s editorial board. Although they are often called the Carcieri tax cuts, and he vigorously supported them, much of the impetus came from General Assembly Democrats like Speaker of the House William Murphy (D-West Warwick) and Majority Leader Gordon Fox (D-Providence). Fox predicted that “this new tax rate, as it did in Massachusetts, is certain to create new jobs, spur economic development, put money back in taxpayers’ pockets, and otherwise bring Rhode Island to a position of twenty-first century economic leadership in the region and, indeed, in the country.” To say that did not happen is a severe understatement.
Income tax cuts for the wealthy at the national level provide mild, if inefficient, stimulus for the economy because they are offset by increasing the national debt. (Of course, there are much better ways to spend our nation’s money.) At the state level, however, it’s a different story. Because state taxes are deductible from national taxes, which tax the wealthy at a higher marginal rate, state level income tax cuts for the wealthy result in increasing national income taxes. The tax cuts also made it harder for Rhode Island to capture revenue from Rhode Island residents who have income in other states. Because so many wealthy Rhode Islanders work in Massachusetts, this is a serious issue. States can only tax out of state income if their tax rate is higher than the tax rate in the other state. So lowering Rhode Island’s income tax rate for the wealthy results in Rhode Island collecting less revenue from other states and other states collecting more revenue from Rhode Island, on top of sending more taxes to Washington. The net result is a considerable flow of capital out of the state, which is not good for the economy.
The real devastation from income tax cuts for the rich, though, comes from the spending cuts and property tax hikes that offset them. The previous section discussed the spending cuts, and how they accelerated after the tax cuts. The next section deals with the property tax hikes.
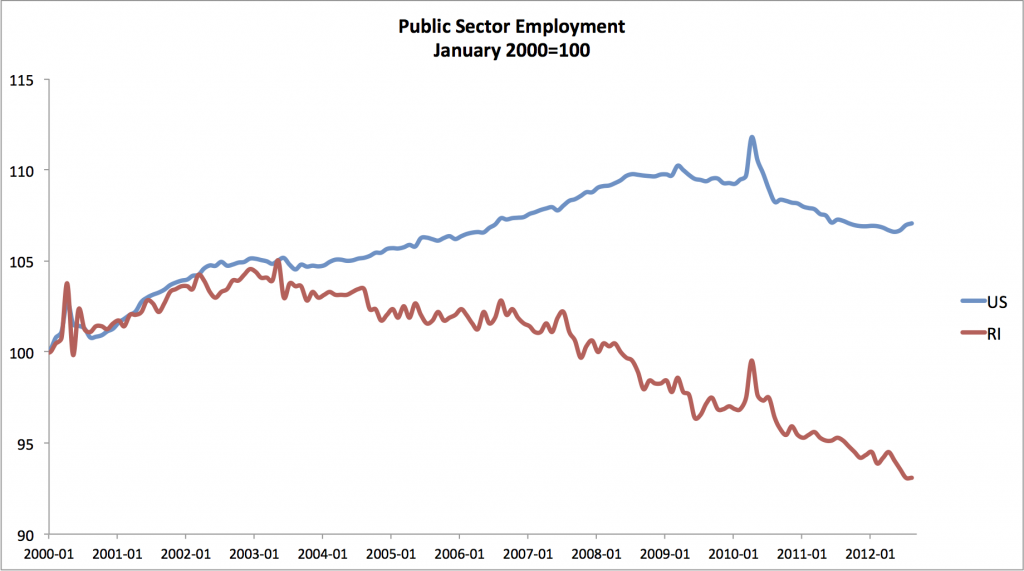
]]>Before Carcieri’s cuts began to bite, Rhode Island public employment tracked the national numbers fairly closely, but once his policies were in place, Rhode Island’s public sector decoupled from the national public sector and took a precipitous nosedive. The bleeding has continued ever since. The pace of the widening of the gap accelerated in late 2006 after the passage of the 2006 budget, with its infamous tax cuts for the rich, but things didn’t end there. Even though public employment began falling all around the country in the aftermath of the recession, we still lost 7.75% of state and local public sector employees between January of 2008 and April of 2012—the second highest drop in the nation.
In conservative junk economics, laying off those greedy public sector workers is always a great idea, but of course, in the real world those layoffs can have devastating effects on the economy. To begin with, the jobs lost in the public sector are themselves jobs the Rhode Island economy has lost. If public employment in Rhode Island had followed the same trajectory as it did in the nation since 2000, we would have almost 9,000 more jobs in the public sector than we do now, and the unemployment rate would be 1.6 percentage points lower. Roughly half of our unemployment gap is the direct result of mass layoffs in the public sector.
The devastation caused by public sector layoffs does not end there. When public workers are laid off, their finances are devastated, and they start spending much less, driving down the demand for goods and services in Rhode Island. They also don’t have the money to buy new houses and can often wind up in foreclosure, which has devastating effects on the housing market. Rhode Island also ceases to benefit from the work that the public sector workers used to do. As Scott MacKay notes, Carcieri oversaw a general breakdown of government services that Chafee has spent much of his term in office trying to clean up.
Everyone has their favorite story of mistreatment at the hands of our government, but mine is the angry letter I received accusing me of not paying my state income tax. When I called up to protest that Rhode Island had already removed the money from my bank account, the woman I finally reached explained to me that they didn’t really have the staff to check whether everyone they were sending these letters to actually hadn’t paid their taxes.
Estimating the magnitude of the collateral damage from Rhode Island’s public sector mass layoffs is difficult, but it is probably fair to say that does not explain all of the rest of the unemployment gap between Rhode Island and the U.S. average. Part of the rest comes from other public sector cuts, many of which were far more savage than the national average. Pensions cuts, stagnant wages, and reduced morale most likely took their toll by reducing demand, but these cuts happened in other states as well, and much of the pain is spread out over several decades, so it remains unclear how much they added to our unemployment gap (probably no more than a few tenths of a percentage point).
Although the Rhode Island media are reluctant to use the word, what happened in Rhode Island was basically European-style austerity. When governments decide to throw out a century of economics and pretend that taking a chainsaw to the public sector will somehow magically not wreck the economy, the results aren’t pretty. This is partially because serious austerity measures like Carcieri’s public sector cuts can lock an economy into the austerity death spiral, where austerity weakens the economy, prompting more austerity. This is a lesson being learned not just in Europe, but also in states like Rhode Island that went all in for the same bad economic policies. All across America, the states that opted for austerity during the recession performed worse than states that did not. When conservative extremist Scott Walker took over in Wisconsin and implemented a severe austerity package that prompted mass protests, Wisconsin’s unemployment rate exploded. A similar wave of job losses is currently blowing through the Northeast region as governments from Maine to Pennsylvania opt for mass layoffs. Because Rhode Island’s recent public sector layoffs have been more in line with the national average, we have largely escaped this regional recession.
Comparing us with the broader Northeast region, however, does not usually paint Rhode Island’s economy in a very flattering light. In fact, because most of the Northeast region did not do as badly as the rest of the country, Rhode Island’s singularly bad record is even worse than it looks. So while public sector cuts explain most of our unemployment gap, alone they do not explain all of it. Some other factor must be at work here, a factor that will be the subject of tomorrow’s post.
]]>In a multi-part series that will be published throughout this week, I’ll get into the weeds on the specific reasons Rhode Island fell behind. A common theme will be how so many (but not quite all) of the problems originated with the man who is now, as Scott MacKay puts it, “retired in his Saunderstown manse by the sea, hiding from the media and the taxpayers he so avidly fleeced.”
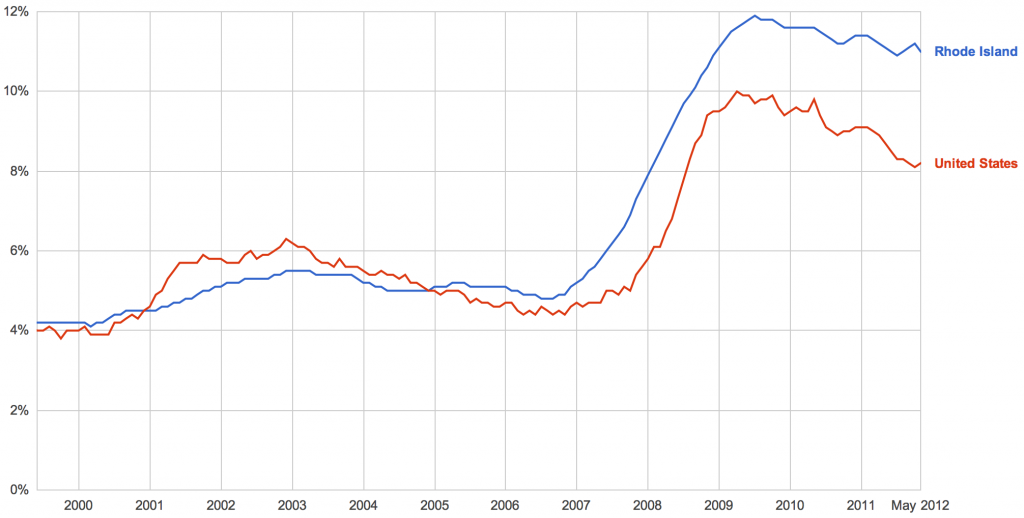
- Rhode Island and U.S. unemployment rates. Data from Bureau of Labor Statistics, via Google Public Data.
Donald Carcieri
A cursory glance at the unemployment rate graph points to a likely culprit. What is perhaps most striking about Rhode Island’s decline is just how closely it corresponds with the tenure of Donald Carcieri. In his first few months, Rhode Island performed reasonably well. As America surged to the peak of the first Bush recession, unemployment jumped half a percentage point between January and June of 2003, but in Rhode Island, unemployment inched up by only 0.2 percentage points.
But giving Carcieri credit for his first few months makes about at much sense as blaming Obama for losing jobs during his first few months. The real test of a leader is how the economy performs once their policies have had a chance to take effect. In mid-2003, things began to turn around. Although America’s recovery was relatively anemic, with the unemployment rate falling by only 1.9 percentage points from the peak of 6.3% in June of 2003 to a low of 4.4% in March of 2007, things went much worse in Rhode Island. During that period, unemployment in our state dropped by only 0.7 percentage points, from 5.5% to 4.8%. In June of 2005, we crossed the national rate. Our jobs picture has been below average ever since.
Up through early 2007, Carcieri’s Rhode Island was in a slow, but not unprecedented, decline. State economies fluctuate, and our slide in the mid-2000s was nothing out of the ordinary. But things were about to get worse. A lot worse. In late 2007, the bottom fell out of the Rhode Island economy, and unemployment soared. Surprisingly, much of the damage was done before the broader US economy began to collapse a little less than a year later.
By April of 2008, when the second Bush recession began in earnest, Rhode Island’s unemployment rate was already at 6.9%—far above the national rate of 5%. Over the next few years, that gap widened from 1.9 percentage points to a peak of 3.3 percentage points in April 2012, but most of the damage was done before the national recession even began. Clearly, something very, very bad happened in Rhode Island in 2006 or early 2007 to spark this collapse.
There is no magical fairy who pummels the economy whenever conservative Republicans find themselves in office. What devastates the economy is the policies they enact. Tomorrow we’ll begin to dig into the details of those policies and why they were so destructive.
]]>