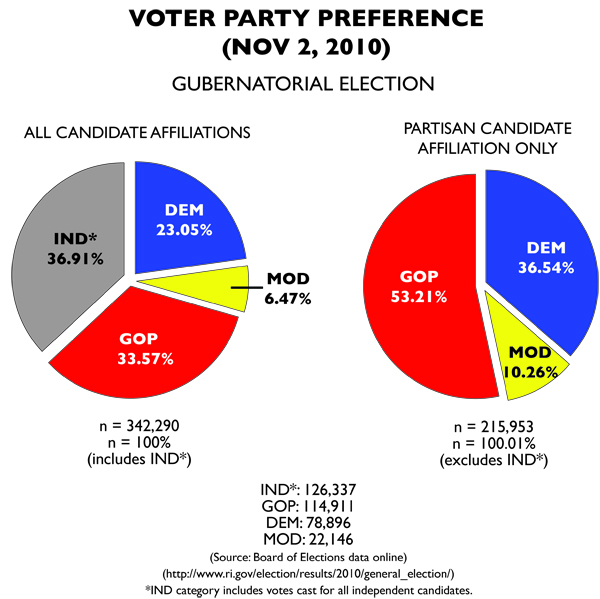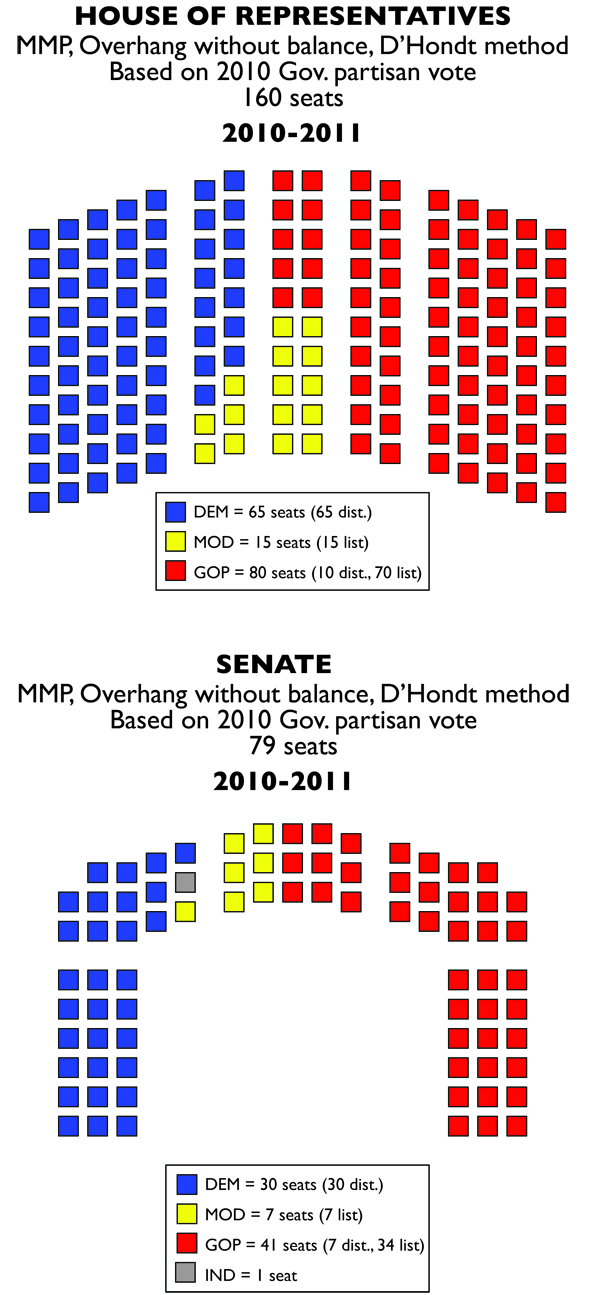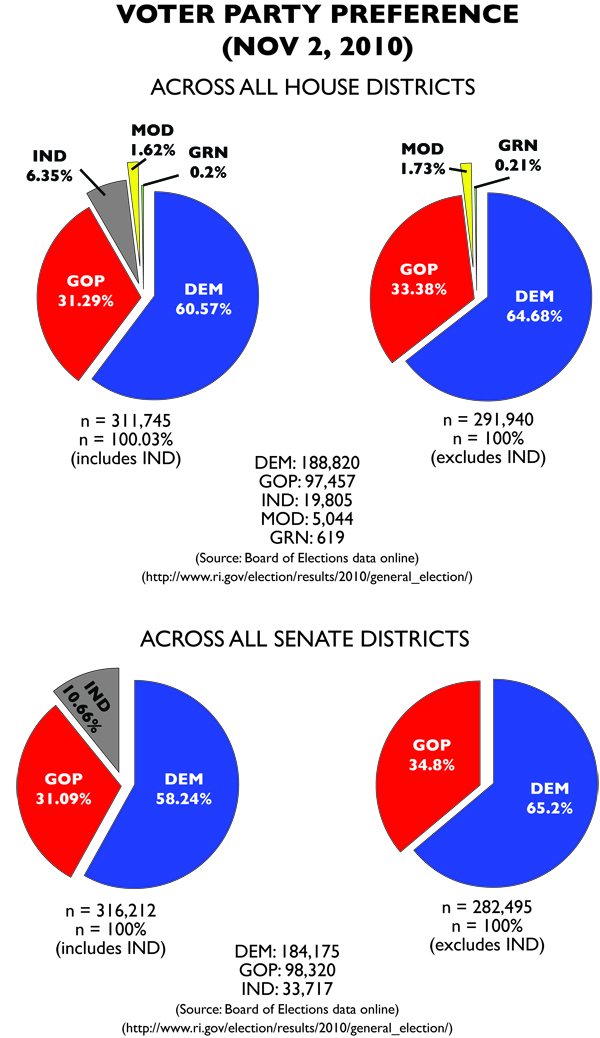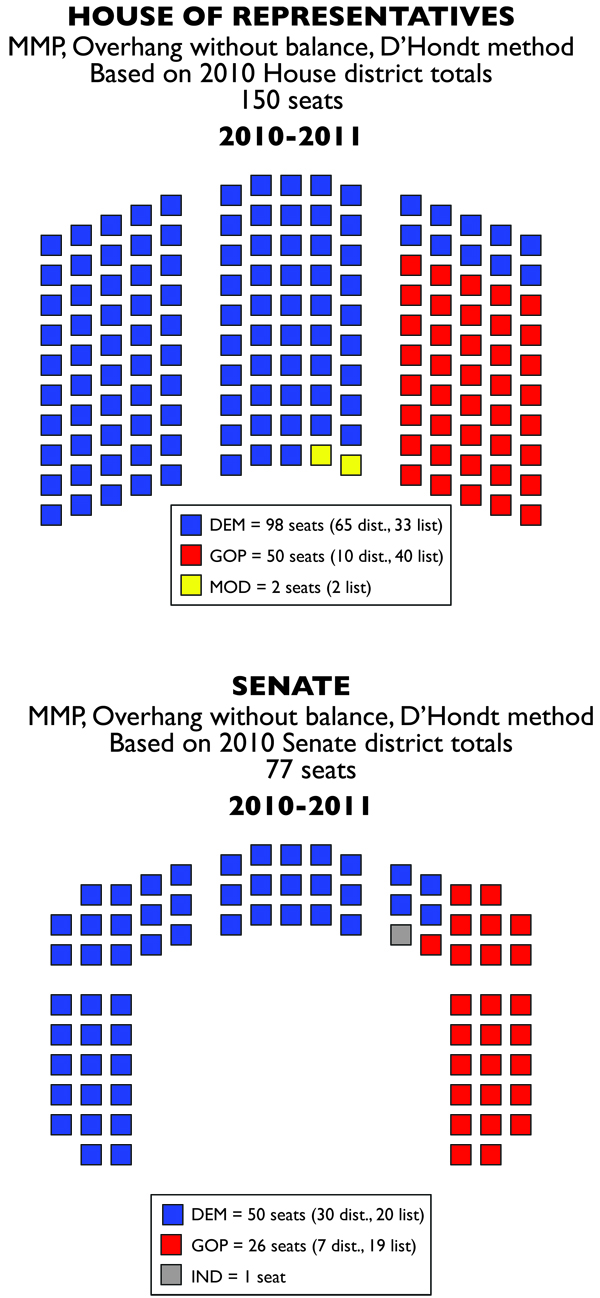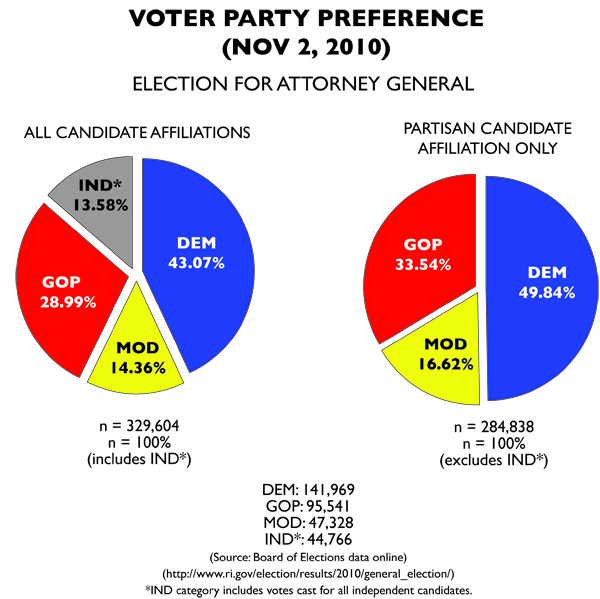
The problem with the gubernatorial results is the massive amount of independent votes that have to be thrown out. Luckily, the AG race offers a more typically Rhode Island affair, though a large amount of independent votes are tossed, but only about equal to what the Moderate Party candidate earned.
That Moderate candidate is the most interesting. The former chair of Common Cause RI and the former President of Save the Bay, lawyer Christopher Little best represented the “environment and ethics” part of the Moderate platform. And his vote performance was better than that of his gubernatorial counterpart Ken Block. Why Little has never been emphasized by the Moderates since is an oddity to me.
If the AG race is used as our party preference ballot, the result is the best case for the Moderates short of winning a majority (which would require a crisis of voter faith).
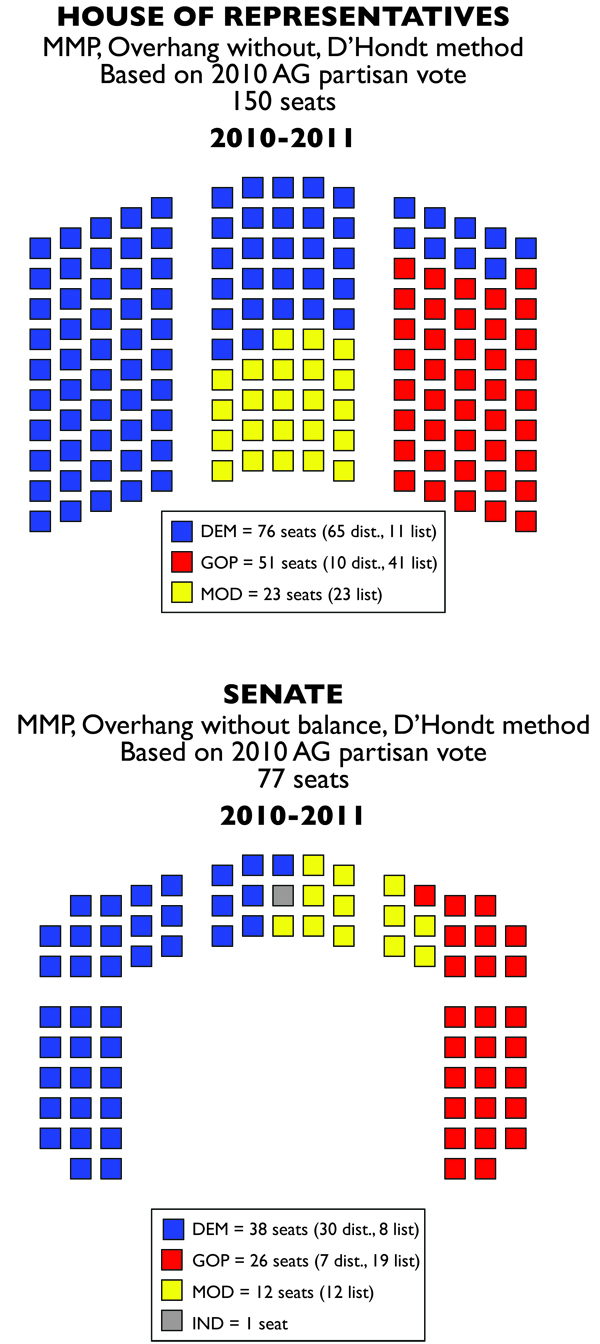
What happens is that the Democrats retain a majority in the House (by one seat only) and have a plurality in the Senate (short by one seat). In this case, the large number of Reps and Senators won by the Moderates can act a drivers of policy. In the Senate, Democrats either have to make a coalition agreement with one of the two parties, or they have to manage to get a leadership team put together with the approval of some members of the other parties or independent Edward O’Neill.
O’Neill’s vote actually becomes very important as well. As an independent, he can be the deciding vote in a showdown between a Moderate-Republican coalition and the Democratic caucus.
The House is a bit different. House Democrats have to be really cautious and not bring any legislation to vote that alienates their caucus and fails to win cross-party support. Otherwise, they could see their leadership team overthrown by a group of disaffected Democratic reps allied with the Moderates and Republicans. Alternatively, they could spurn the left-wing of their party and join with Moderate or Republican legislators to form a cross-party leadership. However, that could damage all parties together, making Republican legislators vulnerable to right wing dissatisfaction, Democratic legislators vulnerable to left wing dissatisfaction, and Moderates vulnerable to voter scorn. How it would shake out would be largely due to personalities.
This is Part 12 of the MMP RI series, which posits what Rhode Island’s political landscape would look like if we had switched to a mixed-member proportional representation (MMP) system in 2002. Part 11 (a revisiting of the 2010 election based on gubernatorial results) is available here. Part 13 discusses other electoral reforms.