 The recent protest outside Juan Noboa’s Olneyville residence by restaurant workers claiming that they were owed thousands of dollars in unpaid salaries for work at his Café Atlantic restaurant has provoked conversation about the propriety of such tactics. Noboa, though his lawyer, denies any wrongdoing and claims that one of his children was “terrified” by the crowd outside his house. His lawyer added that dissatisfied employees should not “protest at a man’s home in the dark” and suggested that a suitable location for protest might be the now closed restaurant.
The recent protest outside Juan Noboa’s Olneyville residence by restaurant workers claiming that they were owed thousands of dollars in unpaid salaries for work at his Café Atlantic restaurant has provoked conversation about the propriety of such tactics. Noboa, though his lawyer, denies any wrongdoing and claims that one of his children was “terrified” by the crowd outside his house. His lawyer added that dissatisfied employees should not “protest at a man’s home in the dark” and suggested that a suitable location for protest might be the now closed restaurant.
It is true that no one would be disturbed by a protest at a closed restaurant. For Noboa and other business owners accused of misconduct by their employees, such an event would be perfect, because the media would not cover it, and no one would have to hear the protester’s demands. Those targeted by such protests and their defenders like to point out that there are proper channels through which to make such complaints. The protesters outside Noboa’s home, with the help of Fuerza Laboral, did file complaints with the Rhode Island Department of Labor and Training, so we can all rest assured, it is argued, that once the system has run its course, justice will be served and Noboa will be compelled to pay, or not, depending on the Dept. of Labor decision.
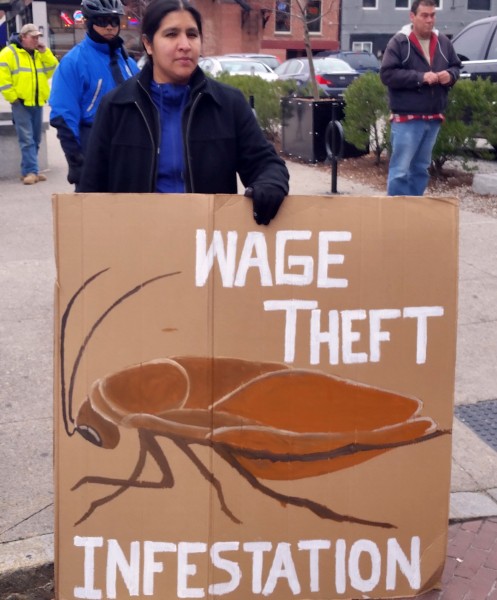 Yet protests like these are not about one business owner who may have stolen wages from employees, or even about two restaurants (the other being Gourmet Heaven, located in downtown Providence and formerly on the East Side) that have closed suddenly, leaving their employees high and dry. These protests are about what Phoebe Gardener, a Community Organizer for Fuerza Laboral, called, “…a pattern of Providence-based food establishments intentionally cheating workers of their wages.”
Yet protests like these are not about one business owner who may have stolen wages from employees, or even about two restaurants (the other being Gourmet Heaven, located in downtown Providence and formerly on the East Side) that have closed suddenly, leaving their employees high and dry. These protests are about what Phoebe Gardener, a Community Organizer for Fuerza Laboral, called, “…a pattern of Providence-based food establishments intentionally cheating workers of their wages.”
Statistics on wage theft are difficult to find. At the Economic Policy Institute (EPI) it is estimated that nationally, wage theft, “is costing workers more than $50 billion a year.” To put that into perspective, the EPI notes that “All of the robberies, burglaries, larcenies, and motor vehicle thefts in the nation cost their victims less than $14 billion in 2012, according to the FBI’s Uniform Crime Reports.” Wage theft is at least three times more costly than all other forms of theft combined, yet our prisons are filled with conventional thieves, not duplicitous employers.
Surveys indicate that most victims of wage theft never sue and never complain to the government. “A three-city study of workers in low-wage industries found that in any given week, two-thirds experienced at least one pay-related violation,” reports EPI, emphasis mine.
Wage theft is widespread, extremely profitable and easy to get away with.
Workers at the low end of the pay scale, or who are socially vulnerable, such as undocumented immigrants or former prisoners, are frequent victims. Reporting the crime of wage theft takes time, time the working poor need to be working in order to survive.
There is little reason for employers to properly pay what they owe workers. If caught, an employer will be ordered to pay the workers what they are determined to owe and may be fined a “maximum civil monetary penalty” of $1,100.
So let’s revisit the tactics of protest.
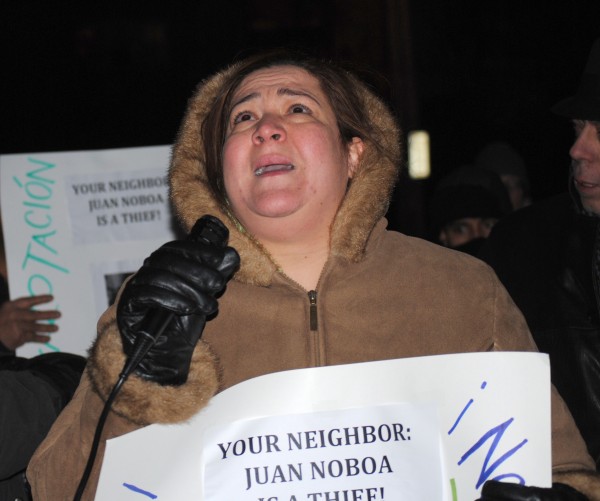 Having protesters arrive outside your home at 6am to accuse you of theft with a bullhorn is embarrassing and may be even a little frightening for your family. The very possibility that this might happen should serve as a deterrent to any business owner in Providence who might be considering cheating employees out of the money owed to them. As the Fuerza Laboral press release stated, “Workers and allies are bringing the message that they must be paid in full immediately or else they will continue to bring public attention on Noboa and the other owners.” [emphasis mine]
Having protesters arrive outside your home at 6am to accuse you of theft with a bullhorn is embarrassing and may be even a little frightening for your family. The very possibility that this might happen should serve as a deterrent to any business owner in Providence who might be considering cheating employees out of the money owed to them. As the Fuerza Laboral press release stated, “Workers and allies are bringing the message that they must be paid in full immediately or else they will continue to bring public attention on Noboa and the other owners.” [emphasis mine]
Workers, who used to be all but powerless in these situations, are finding ways to shift the playing field. This doesn’t mean that workers suddenly have the advantage, far from it, but if workers continue to use such tactics, business owners will no longer be able to steal from their employees so easily. Now offending employers risk something much more valuable than money: Their public reputations and the respect of their neighbors and family.
Laws could be passed that strengthen the rights of workers and make it easier to file claims of wage theft. Fines and penalties for non-payment or underpayment of wages could be increased to the point where they act as real deterrents, rather than as a cost of doing business. Our legislature could enact legislation that makes it economically worthwhile for unpaid employees to pursue their rightful claims.
However, in the absence of thoughtful legislation that protects the rights of workers, public protest must fill in to loudly proclaim a simple truth: Workers have dignity and deserve to be treated with respect.




 From the headlines, you would think that CNBC is the gold standard economic authority. After the cable news network released its 10th annual “
From the headlines, you would think that CNBC is the gold standard economic authority. After the cable news network released its 10th annual “

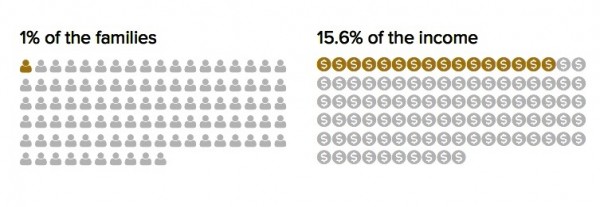 “Rising inequality is not a new phenomenon, and it’s not confined to large urban areas or financial centers,” said Price. “It’s a persistent problem throughout the country—in big cities and small towns, in all 50 states. In the face of this national problem, we need national policy solutions to jump start wage growth for the vast majority.”
“Rising inequality is not a new phenomenon, and it’s not confined to large urban areas or financial centers,” said Price. “It’s a persistent problem throughout the country—in big cities and small towns, in all 50 states. In the face of this national problem, we need national policy solutions to jump start wage growth for the vast majority.”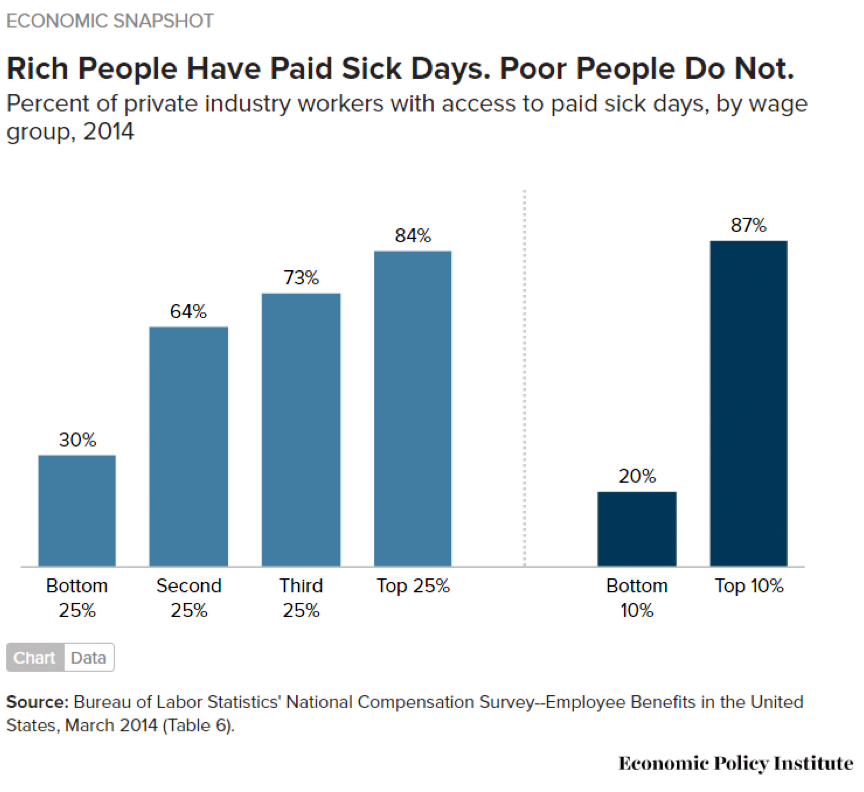
 One significant reason to pass paid sick leave legislation is that failing to do so further exacerbates disparities based on income. The Economic Policy Institute
One significant reason to pass paid sick leave legislation is that failing to do so further exacerbates disparities based on income. The Economic Policy Institute 
 W
W
 Over the weekend the
Over the weekend the 

 The recent
The recent  Yet protests like these are not about one business owner who may have stolen wages from employees, or even about two restaurants (the other being
Yet protests like these are not about one business owner who may have stolen wages from employees, or even about two restaurants (the other being  Having protesters arrive outside your home at 6am to accuse you of theft with a bullhorn is embarrassing and may be even a little frightening for your family. The very possibility that this might happen should serve as a deterrent to any business owner in Providence who might be considering cheating employees out of the money owed to them. As the Fuerza Laboral press release stated, “Workers and allies are bringing the message that they must be paid in full immediately or else they will continue to bring public attention on Noboa and the other owners.” [emphasis mine]
Having protesters arrive outside your home at 6am to accuse you of theft with a bullhorn is embarrassing and may be even a little frightening for your family. The very possibility that this might happen should serve as a deterrent to any business owner in Providence who might be considering cheating employees out of the money owed to them. As the Fuerza Laboral press release stated, “Workers and allies are bringing the message that they must be paid in full immediately or else they will continue to bring public attention on Noboa and the other owners.” [emphasis mine]