 Between 2009 and 2013, the top one percent captured 85.1 percent of total income growth in the United States. To be included in the top one percent in Rhode Island your annual income would have to be $336,625. The average income of a Rhode Island one-percenter is $884,609. Since the bottom 99 percent makes $47,545 on average, the top one percent makes 18.6 times more than the bottom 99 in this state.
Between 2009 and 2013, the top one percent captured 85.1 percent of total income growth in the United States. To be included in the top one percent in Rhode Island your annual income would have to be $336,625. The average income of a Rhode Island one-percenter is $884,609. Since the bottom 99 percent makes $47,545 on average, the top one percent makes 18.6 times more than the bottom 99 in this state.
This info is gleaned from Income inequality in the US by state, metropolitan area, and county, a new paper published by the Economic Policy Institute (EPI) for the Economic Analysis and Research Network (EARN). The paper, by Mark Price, an economist at the Keystone Research Center in Harrisburg, Penn. and Estelle Sommeiller, a socio-economist at the Institute for Research in Economic and Social Sciences in Greater Paris, France, shows that the top one percent of income earners captured the majority of income growth since the Great Recession in 24 states—with the top one percent taking home all income growth in 15 states.
Rhode Island ranks 28 out of the states in income inequality, based on the ratio of top one percent to bottom 99 percent income. The situation in Massachusetts (ranked 6) and Connecticut (ranked 2) is far worse for inequality.
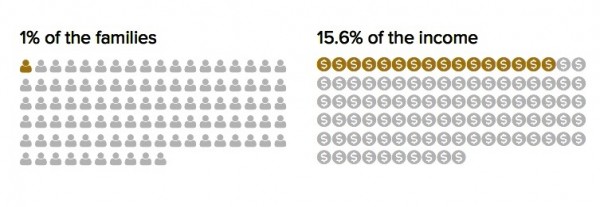
The top one percent in Rhode Island takes 15.6 percent of all income in Rhode Island. This number approaches or surpasses historical highs, tracked from 1917-2013.
 “Rising inequality is not a new phenomenon, and it’s not confined to large urban areas or financial centers,” said Price. “It’s a persistent problem throughout the country—in big cities and small towns, in all 50 states. In the face of this national problem, we need national policy solutions to jump start wage growth for the vast majority.”
“Rising inequality is not a new phenomenon, and it’s not confined to large urban areas or financial centers,” said Price. “It’s a persistent problem throughout the country—in big cities and small towns, in all 50 states. In the face of this national problem, we need national policy solutions to jump start wage growth for the vast majority.”
“The degree of income inequality differs from one city to another, but the underlying forces are clear. Inequality isn’t a regional issue. It’s the result of intentional policy decisions to shift bargaining power away from working people and towards the top 1 percent,” said Sommeiller. “To reverse this, we should enact policies that boost worker’s ability to bargain for higher wages, rein in the salaries of CEOs and the financial sector, and prioritize full employment.”

