President Obama released his 141 page ‘policy and wish list” when he unveiled his politically ambitious FY 2016 budget on Feb 2, not having to worry about running for president in the upcoming 2016 presidential election cycle.
President Obama released his 141 page ‘policy and wish list” when he unveiled his politically ambitious FY 2016 budget on Feb 2, not having to worry about running for president in the upcoming 2016 presidential election cycle.
Yes, even inside the Washington Beltway a picture is truly worth a thousand words. Gone is the budget’s plain blue cover replaced by a black and white photo of the Tappan Zee Bridge in New York, an image that projects one of the President’s spending priorities of rebuilding the nation’s infrastructure to create jobs and improve the transportation system.
The $4 trillion presidential budget, a political campaign document outlaying his policies and priorities, would cancel automatic sequestration cuts to domestic and military programs over a 10 year period. According to the New York Times, Obama’s budget proposal would add $6 trillion to the national debt, and the single-year deficit would rise to $687 billion by 2025.
Obama’s FY 2016 budget puts more funding into education, rebuilding the nation’s infrastructure, increased defense spending, along with providing tax relief for America’s middle class while increasing the taxes for corporate America and the wealthy. Political insiders say that Obama’s budget, one that gives to the middle class and assesses higher taxes from corporate America and the wealthy, sets the issues to be surely debated in the upcoming presidential election. .
A Look at Aging Priorities
In a Feb. 3 blog post, Nora Super, executive director of the upcoming White House Conference on Aging, details how the recently released budget proposal will “ensure that older Americans enjoy not only longer but healthier lives.”
As to retirement security, Super notes that the Obama Administration strongly opposes any legislative measures that would privatize the nation’s Social Security program, or slash benefits for future generations or reduce basic benefits to current beneficiaries. Super says that half the nation’s workforce, that’s about 78 million, does not have a retirement savings plan at work. “Fewer than 10 percent of those without plans at work contribute to a plan of their own. The President’s FY 2016 Budget expands retirement opportunities for all Americans to help families save and give them better choices to reach a secure retirement,” she says.
According to Super, Obama’s Budget proposal supports healthy aging by strengthening the Medicare program by “aligning payments with the costs of providing care, along with encouraging health care providers to deliver better care and better outcomes for their patients, and improving access to care for beneficiaries.”
To put the brakes to rising prescription drug costs, Super notes that the President’s Budget proposes to close the Medicare Part D donut hole for brand drugs by 2017, rather than 2020, by increasing discounts from the pharmaceutical industry. The Budget proposal also gives the Secretary of Health and Human Services new authority to negotiate with drug manufacturers on prices for high cost drugs and biologics covered under the Part D program.
Linking nutrition to healthy aging, Super says that Obama’s Budget provides “over $874 million for Nutrition Services programs, a $60 million increase over the 2015 enacted level, allowing States to provide 208 million meals to over 2 million older Americans nation-wide, helping to halt the decline in service levels for the first time since 2010.” Also, Obama’s budget ratchets up funding for supportive housing for very low-income elderly households, including frail elderly, to give these individuals access to human services, she adds. .
Protecting older persons from elder abuse, neglect and financial exploitation, Super blogs that the President’s budget proposal includes $25 million in discretionary resources for Elder Justice Act programs authorized under the Affordable Care Act. “Funding will “improve detection and reporting of elder abuse; grants to States to pilot a new reporting system; and funding to support a coordinated Federal research portfolio to better understand and prevent the abuse and exploitation of vulnerable adults,” she says.
Here’s Super’s take on the Obama budgetary blueprint: “Taken together, these and other initiatives in the Budget will help to change the aging landscape in America to reflect new realities and new opportunities for older Americans, and they will support the dignity, independence, and quality of life of older Americans at a time when we’re seeing a huge surge in the number of older adults.”
In a released statement, AARP Executive Vice President Nancy LeaMond gives thumbs to the president’s efforts to “lower the cost of prescription drugs, promote better care, reward improved outcomes and make health care programs more efficient and less wasteful.” She also expresses her nonprofit group’s support for the President’s budgetary priorities to “create opportunities for the middle class” and his goal “to make saving for retirement easier.”
But, LeaMond expresses concerns that higher premiums, deductibles and copays might shift costs to older Americans. “As the federal deficit continues shrinking, we must find responsible solutions for strengthening critical programs and improving the retirement and overall economic security of current and future generations. We must also look for savings throughout the entire health care system, as the rising cost of health care threatens people of all ages,” she says.
In his statement, President/CEO Max Richtman, of the Washington, DC-based National Committee to Preserve Social Security and Medicare, agrees with LeaMond’s concerns of higher premiums, deductible’s and co pays, too. “While some tout increasing means testing in Medicare as a way to insure ‘rich’ seniors pay their share, the truth is, the middle-class will take this hit as well,” he predicts.
Political pundits say that Obama’s 2016 budget was dead-on arrival at Capitol Hill the day it was released at the beginning of February. In the shadow of the upcoming 50th Anniversary of Medicare, Medicaid, and the Older Americans Act, as well as the 80th Anniversary of Social Security, GOP leadership in both chambers of Congress must work with the Democratic President to hammer out a bipartisan compromise. Putting budgetary proposals that strengthens the nation’s programs and services for older Americans on the chopping block for purely political reasons is not acceptable, especially to a nation that opposes political gridlock.
Herb Weiss, LRI ’12, is a Pawtucket-based writer covering aging, health care and medical issues. He can be reached at hweissri@aol.com.
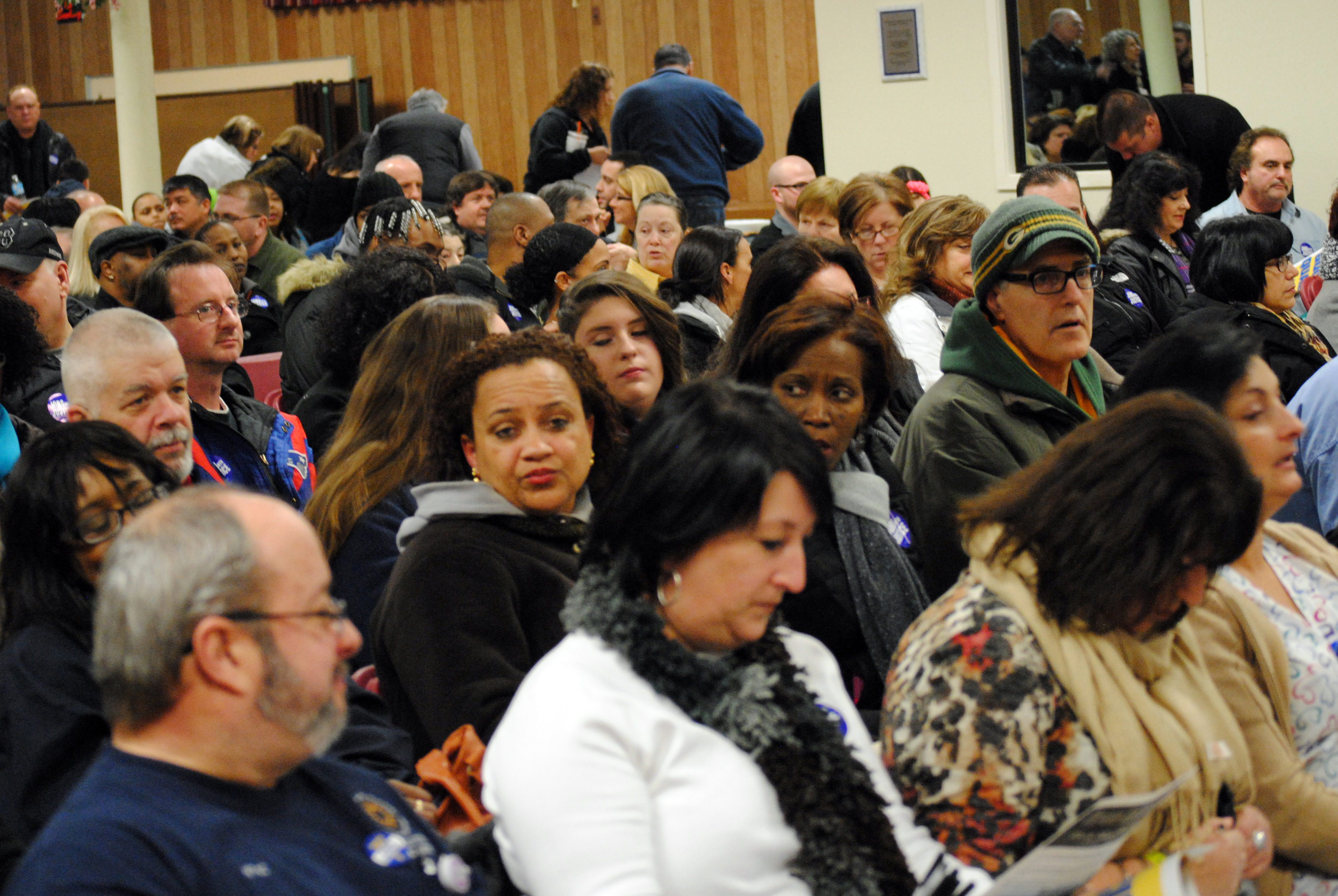



 More than 500 people crowded into the meeting room of Our Lady of the Rosary Church on Benefit St in Providence for the
More than 500 people crowded into the meeting room of Our Lady of the Rosary Church on Benefit St in Providence for the  According to Local 251, “As a non-profit entity, Lifespan and RI Hospital are supposed to put the healthcare needs of the community first. Unfortunately, management has taken cost cutting measures, causing shortages in equipment and staff that undermine patient care.”
According to Local 251, “As a non-profit entity, Lifespan and RI Hospital are supposed to put the healthcare needs of the community first. Unfortunately, management has taken cost cutting measures, causing shortages in equipment and staff that undermine patient care.” Obamacare has allowed Lifespan/RI Hospital to take in an additional
Obamacare has allowed Lifespan/RI Hospital to take in an additional  The Speakout was intended to show community support for the workers of RI Hospital, and was attended by Representatives David Cicilline and Jim Langevin, as well as General treasurer Seth Magaziner. There were also representatives from many other unions and community groups such as Jobs with Justice, Unite Here! and Fuerza Laboral. Many religious leaders, including Father Joseph Escobar and Rev Duane Clinker, were on hand to show support.
The Speakout was intended to show community support for the workers of RI Hospital, and was attended by Representatives David Cicilline and Jim Langevin, as well as General treasurer Seth Magaziner. There were also representatives from many other unions and community groups such as Jobs with Justice, Unite Here! and Fuerza Laboral. Many religious leaders, including Father Joseph Escobar and Rev Duane Clinker, were on hand to show support.