Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Last Wednesday, RIDOT presented what it is calling a “boulevard-highway hybrid” model of the 6/10 Connector. I’ve dubbed their proposal “6/10 Dig” because it replicates the mistakes of the “Big Dig” in Boston. Our proposal at Moving Together Providence continues to be a true 6/10 Boulevard. Kevin Proft at Eco RI News has done the best comprehensive coverage of this topic of anyone in the media so far, and even I can’t try to reconvene all the information he put together, so please check out his piece.
There are many people who would benefit from the 6/10 Boulevard, but why should drivers support it over the 6/10 Dig option?
RIDOT is wrong. . . It’ll take too long. . .
Cost
A boulevard is a hybrid by nature. The nonsense “highway-boulevard hybrid” name really just means a capped highway, like the Big Dig. The Big Dig was the most expensive highway project in U.S. history. While the Big Dig produced a really nice park for downtown Boston, it left the problems of the highway untouched elsewhere. The same will be true for a 6/10 Dig.
Why is a boulevard cheaper? The 6/10 Connector highway is full of bridges that need to be fixed, and those bridges span parts of the highway itself, as well as over the highway. If we built a boulevard, we could build bridges only over the Northeast Corridor tracks, and that would make the bridges 80% shorter.

The capping process for RIDOT’s 6/10 Dig also essentially requires digging and covering two tunnels, in a river valley floodplain. This inherently adds all sorts of unforeseen and difficult-to-predict costs that are not part of a boulevard project. The Alaskan Viaduct, which Washington State’s DOT forced down the throat of Seattle after ignoring two referenda that rejected it, is currently an example of how this can go horribly wrong. Big Bertha, the tunneling device that was specially made to dig the Alaskan Viaduct, has gotten stuck several times. There is also ominous settling of buildings in Seattle’s downtown, suggesting that the tunnel may be undermining the foundations of the buildings. These cost overruns in Seattle are a warning against this approach, just like the numerous cost overruns in Boston were.

The 6/10 Dig also keeps a highway form to the road, which means it needs exit and entrance ramps. That not only means spending money to build and maintain those ramps, but it means negatively affecting the development pattern for 70 acres of land that would be available in a boulevard model for development.
RIDOT’s 6/10 Dig proposal: spend more to do an uglier job that will leave less potential to earn taxable income in the future.
Moving Together’s proposal: save now, do a nicer job, and add potential development. We also support reducing the toll amounts to reflect whatever surpluses become available from our model.
Congestion
 A few people have started to send me angry tweets or emails about how I’m attempting to drive them out of their car. And while I would very much welcome people choosing to drive less, as evidenced by lots of my writing, I’d like to remind people that you can drive on a boulevard. In fact, boulevards originally were a widening of streets that had been much narrower. The Champs Elysée was thought up by Emperor Napoleon III to prevent further revolutions in France’s capital. Today it carries 60,000 cars and 500,000 pedestrians a day.
A few people have started to send me angry tweets or emails about how I’m attempting to drive them out of their car. And while I would very much welcome people choosing to drive less, as evidenced by lots of my writing, I’d like to remind people that you can drive on a boulevard. In fact, boulevards originally were a widening of streets that had been much narrower. The Champs Elysée was thought up by Emperor Napoleon III to prevent further revolutions in France’s capital. Today it carries 60,000 cars and 500,000 pedestrians a day.
Why does a highway work less well for cars than a boulevard? First off, we’re talking about urban highways. A rural highway is a totally appropriate piece of infrastructure that carries cars quickly. An urban highway fails because it blocks many of the advantages that cities have to deal with traffic.
The East Side is a part of Providence that has been (relatively) less affected by highways than other parts of the city. It does have I-195 cutting across its waterfront, which carries its own issues, but unlike Downtown Providence or the West Side, Olneyville, and Silver Lake, it has no highways cutting it directly off from other parts of itself.
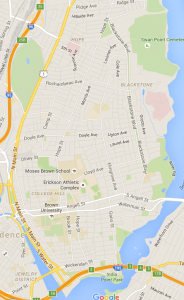
Wouldn’t an Angell Street Expressway improve traffic congestion? After all, the East Side has some of the largest employment centers in the state, and because many of the jobs it serves are high-income, a sizable portion of its workforce chooses to live outside the city and commute by car. A hypothetical Angell Street Expressway helps to explain what’s going on in Olneyville with traffic.
If you look at a map of the East Side, you’ll see that north-south there are fifteen pairs of streets between Butler and Main Street, inclusive. That’s fifteen streets, each with two lanes.
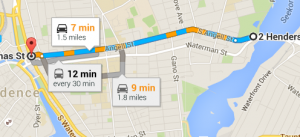
Google says it would take 7 minutes to go up Angell Street at the current speed limit. Having an expressway might half that time, in theory.
But what of those north-south trips? In order to make the highway work at high speed, it would have to be limited-access, meaning that it would have only a few entrances and exits. All of the traffic that currently flows through 30 lanes of small streets would have to cross the highway at odd intervals– perhaps at Main St., Hope St., and Gano St.
This would be a disaster, but that wouldn’t be the only thing about the Angell Street Expressway that would be messed up for drivers.
A hypothetical Angell Street Expressway would need exit- and entrance-ramps for those three stops. I took a screenshot of an area of the map roughly the size of the Viaduct and placed it over Thayer Street. There’d be a second one like this on the other side. Several blocks of housing and businesses would have to be removed in between the exit- and entrance-ramps, for the full length of the highway. And two more sets of exit- and entrance-ramps would be needed at Main and Gano, respectively.
Would this have a further effect on driving times? Of course. Currently, many people walk on the East Side, and that contributes to the fact that Thayer Street is lively even sometimes during blizzards, and can have tremendous success drawing people for business when the street is closed to cars. Suddenly every trip would need to be driven. And the lack of a grid would mean that people who were driving short trips would take the highway to get around and through this maze.
The East Side is not perfectly uncongested, especially on Thayer Street itself, which is very popular, and narrow. But doesn’t it seem odd that a part of the city where the most employment and economic activity is happening manages without an Angell Street Expressway, but Olneyville– a part of the city that is depressed, and has a nearly 50% non-car-ownership rate, but no major industries– has constant traffic? Olneyville Square at 3:30 on a Wednesday looks like Thames Street on 4th of July in Newport, but with none of the apparent economic activity driving that congestion.
A capped highway could connect some streets, because the connective parkland built over the highway might be wide enough to slightly expand the range of choices to drivers. But it would do so at great cost now, and into the future, and so the number of bridges that could be built would be limited. A boulevard, because of its low cost, could reconnect almost all the streets on either side, and at much less cost. And what that means is that instead of having to sit through Olneyville Square to get to a highway that will be almost as backed up, you can glide along a number of streets in a connected neighborhood.
A Tested Idea

We’ve already been here, and it wasn’t any flower-sniffing hippie that brought us there. The late Buddy Cianci moved train tracks and a river to put together Memorial Blvd and Waterplace Park, both of which have been successful by any measure. But because of the weird engineering choices that had to go into those projects, they were obviously very expensive. By contrast, the 6/10 Boulevard project does something we’ll have to do one way or another: tear down the old 6/10 Connector. The only thing that is different is it calls for not rebuilding the monstrosity. By saving money, we can lower tolls. We can add development land to the tax revenue of the state and city. But we can also better support drivers by removing the old grey wall that currently stands in their way.
~~~~
UPDATE: Addressing some other concerns.
The Great Northwest Passage
Lewis & Clark, here I come.
Boulevard proponents do not intend to remove the whole of Rt. 6. This is something that keeps coming up as a concern, and that is something I want to address here.
It’s It’s It’s understandable for people not to know this, since everyone in the state shouldn’t be expected to live and breathe the 6/10 Connector as I do, but the Moving Together Providence proposal does not make any changes to the northwest corridor of Rt. 6. Our proposal calls for the boulevard to transition back to a highway somewhere around Hartford Avenue north. Where the map cuts off to the northwest is roughly where such a transition to a highway could go. It’s not nearly as harmful to have Rt. 6 along the edge of Manton into Johnston as it is to have it cut through other parts of the city as the 6/10 Connector, because there are not meaningful historic commerce or community connections being blocked. The Woonasquatucket Greenway already exists parallel to this section of highway.

Justin Katz of Ocean State Current-Anchor happily surprised me when he endorsed the idea that the people of Providence should have the greatest say in the form of the 6/10 Connector, and that spurred a conversation in the comments section of his post. Commenters ShannonEntropy and Tom Hoffman brought up issues related to the interests of suburban commuters, citing the lack of a good “east-west” route (ShannonEntropy’s words). Hoffman, who has written in support of the boulevard as part of the labor-oriented Common Ground RI, did not mention an east-west connection in his comments on the piece, but has brought this issue to me in other conversations.
The search for the Great Northwest Passage led Lewis & Clark astray, and I think this concern is also wrongheaded here. Just to illustrate the point, let’s look at a density map of Rhode Island.
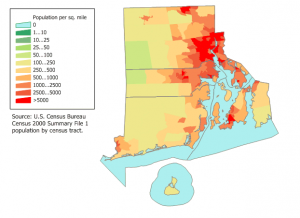
Yes, it’s clear that commuters from the northwest of the state use Rt. 6 if they want to come into the city– and they should continue to. No one– let me repeat that– no one is trying to get you to stop driving to Providence from Johnston or points northwest.
The issues that plague the 6/10 Connector don’t emanate from Johnston commuters. They emanate from the huge number of local trips that are misplaced onto the Connector by a lack of a street grid. All of the commuters from the northwest of the state could try getting on the highway at once, and my feeling is that even together, they’d have a hard time creating a traffic jam, but if even a small number of Providence residents are pushed onto the highway for the short trips they’re taking between neighborhoods, it would create a traffic jam. That’s what happens everyday.
There’s an enduring dream of a Great Northwest Passage out of Providence and across the state, and some wish that that passage would have also connected with I-84. I think that would be a mistake as well. The natural, self-organizing nature of commuter and residency habits has created no problem here. The 6/10 Connector has. If we’d knocked through the rural hinterlands of the state with an expensive highway addition, we would be causing Big Government to redefine and socially engineer that reality away from what it is.
How to transition?
How is this done? One of the cheapest, more congestion-fighting, and safest ways to transition a high-speed road to a lower-speed one is a roundabout or traffic circle.
Traffic circles have downsides, particularly for cyclists, which is why in the Netherlands, cyclepaths are usually routed around them. But for transitioning the edge of a city into a highway, roundabouts create a highly efficient compromise between pedestrian and car needs, which also costs a lot less than signaling. State DOTs like Wisconsin’s require roundabouts as the first consideration for all newly designed intersections, in part because they save money, and in part because they reduce the incidence and severity of crashes.
The example I use above is somewhat different than what I have in mind, but still illustrates the self-organizing nature of traffic in a traffic circle. The actual implementation of the idea as a transition point between highway and boulevard would differ because it would not be in the center of town, but rather on the edge of urban development towards something else. Philadelphia’s Eakin’s Oval– a transition between the very fast Kelly Drive/East River Drive and the boulevard-like Benjamin Franklin Parkway– and Logan Circle– the second transition, between the faster part of the Parkway and the much slower, more urban part near Philadelphia’s City Hall.
If you think, “Gee, the Ben Franklin Parkway doesn’t look that urbanist to me” you’re right. Jane Jacob’s hated the Ben Franklin Parkway, which she identified in The Death and Life of Great American Cities as a big-planner departure from the more organic street form of Philadelphia around places like Rittenhouse Square. But that’s the point, in a way: a boulevard is not perfect urbanism. It’s a compromise point between the needs of drivers to drive in the city, and the needs of the city to be a city. The Ben Franklin Parkway isn’t my favorite part of Philadelphia as a native of that region, but it is a beautiful and enjoyable one, and economically productive. It features widely on postcards of Philadelphia, as the endpoint of the famous “Rocky Steps” of the Museum of Art.

A failed vision
We should not use the most expensive item in our pantry for every purpose, but that does not make that item bad. The distortion of the American diet, many have pointed out, comes not from the “bad” foods we eat being “bad for us” so much as from the weirdly top-down planning that makes those foods everyday fare. This same paradigm affects driving, and transit.
Just to show you that I’m not biased against driving, let me give you a transit waste example.

The transit planner Jarrett Walker, out of Portland Oregon, produced a stunning redesign of Houston’s bus system. The Houston system had been bleeding ridership for many years, and Walker redesigned the system to be more comprehensive, more frequent, and more convenient, while not spending any extra money on it. Naturally this involved some tradeoffs, but the vast majority of previous riders of Houston’s buses continue to use the same bus stop now that the system has changed. Ridership is now increasing, instead of decreasing.
Walker has described how members of the public whose bus stop did change sometimes did not like the fact that they had to walk an extra quarter mile to get to the route, not understanding that buses don’t simply represent lines on a map, but also lines that have other dimensions– like frequency and span. If you have two buses to choose from, but they’re half as frequent, and their resultant low ridership means they stop at 7 PM instead of 12 PM, then the two buses are a less useful service than just one.
A bus is a cost-effective service if used right, but it’s also an expensive service that requires on-going maintenance and labor costs. Using the most expensive item in your toolbox– a bus– to meet the needs of a pedestrian trip does not make sense, especially if spreading those resources undermines both.
People often say I’m “the bike guy” because they misunderstand my point about bike routes. Bike routes an inexpensive tool, so the more we can meet the needs of commuters on bikes, and then use our more expensive tools like roads and buses sparingly, the better we’re able to marshall our resources to the best result for taxpayers and commuters.
If you want to meet the needs of disabled people, for instance, you could spread your bus resources really thin, and provide a bad bus service for everyone, or you could create a few very good buses for the same cost, but use the savings to fill the gaps with good pedestrian and bicycle infrastructure.
The failed vision of RIPTA is often to stop in each nook and cranny, to turn into each parking lot, to hit each 100 foot gap, and by doing so make the route take forever and work for no one but the most desperate. A better vision would have RIPTA marshall its resources towards the highest uses, and let bicycles and sidewalks fill in the gaps.
How that failed vision applies to roads
Urban highways were a utopian vision by planners like Le Corbusier. Here was Le Corbusier’s vision for Paris:
Y
You can see not only that this is an awful vision, but that it resembles the 1960s Big Government views of people like Robert Moses. What Le Corbusier misunderstood was that the apparent efficiency of highways doesn’t work in the context he imagined it. He forgot parking, he forgot traffic congestion, and most of all he forgot that highways are the dollop of expensive whipped cream on the pancake, not the pancake itself.
The RIDOT 6/10 Dig proposal reminds of this 1920s era, when planners thought they could direct each activity from above with unlimited resources. It’s an entrancing vision, actually, and if you forget how much it would cost, or how many resources it would swallow, you can almost see why it seemed like a great idea.
In a bus, the bus is the expensive option, and walking or biking is the final connection. They exist together. With a highway, the highway is the expensive option, and driving a city street is the final connection. To imagine that all the city streets would disappear into huge Jetsons-like highways, with towers-in-the-park between them, is wrong.
Why a boulevard?
A boulevard makes the most sense because it rejects the utopianism of Le Corbusier, and instead uses highways as the tool they’re meant for– long-distance travel between two productive places. The boulevard reconnects streets. Yes, there are commuters from the northwest, and because they come from suburban and rural areas, it is very likely that many of them if not all of them will continue to drive post-boulevard. But because their numbers are less great than our intuition says, that’s actually not a problem. The goal of a boulevard, or of any urbanist project, is not to force people not to drive, but to create the right set of options so that driving doesn’t become the only way around. Let’s take our heads out of the 1920s’ futurism, and build the 6/10 of today.
~~~~