President Obama’s first term had devolved into the massive bungling of the Affordable Care Act. Republican intransigence in Washington combined with Obama’s refusal to stake out positions for his healthcare reform left Democratic partisans confused and disheartened. Meanwhile, Republicans were rallying against any change, and they had fired themselves up into a new movement, the Tea Party.
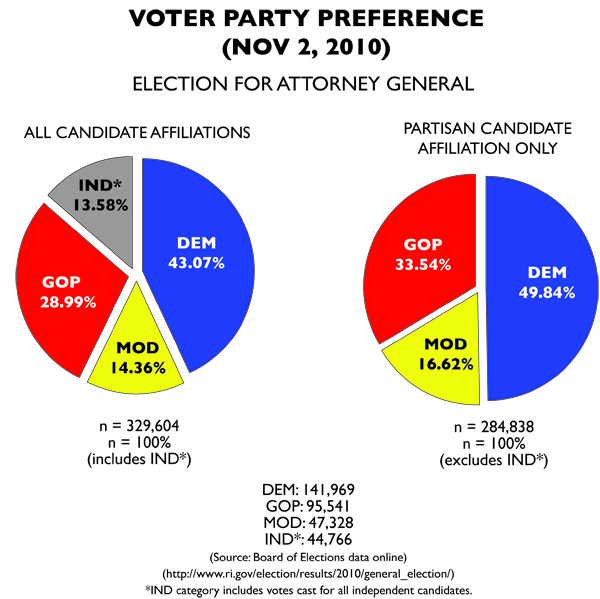
In Rhode Island, the situation was more confused. While the Republicans had nominated outgoing Gov. Carcieri’s senior communications advisor, the Democrats had selected General Treasurer Frank Caprio. Meanwhile, Ken Block was running at the top of the ticket for Rhode Island’s newly minted third party, the Moderates. But the candidate who had the most name recognition was former US Sen. Lincoln Chafee.
Since his defeat in 2006, Chafee had unaffiliated and back Barack Obama’s election in 2008. He would go on to narrowly win the Governorship, after Caprio insulted the President and it made national news. Staunch Democratic voters were left with little choice but to choose Chafee, the man they had rallied to defeat merely four years before.
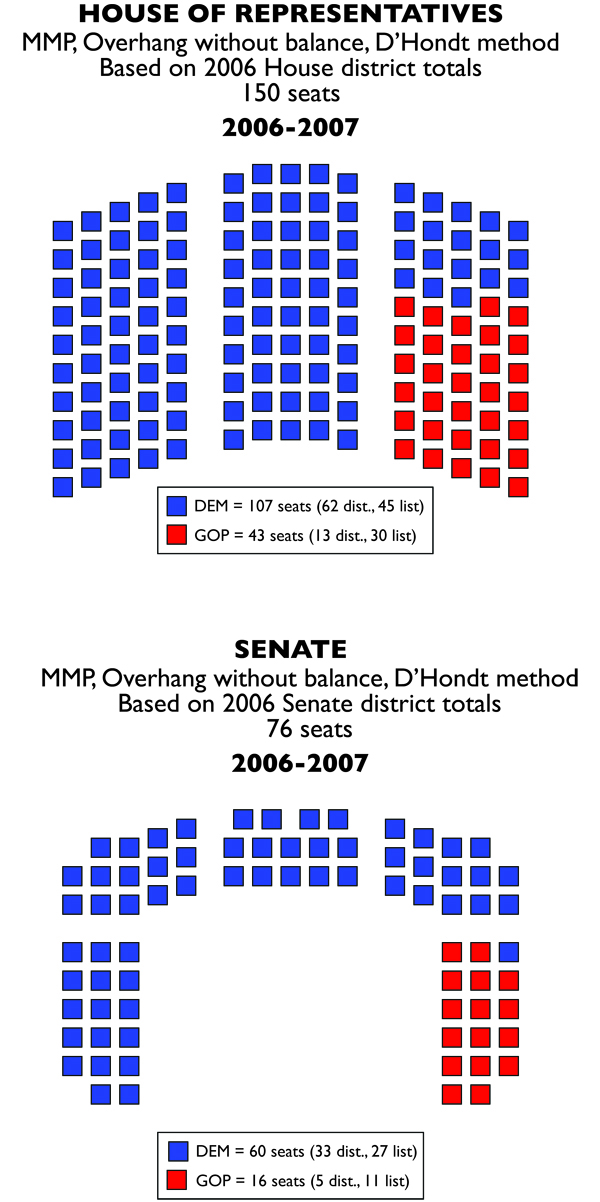
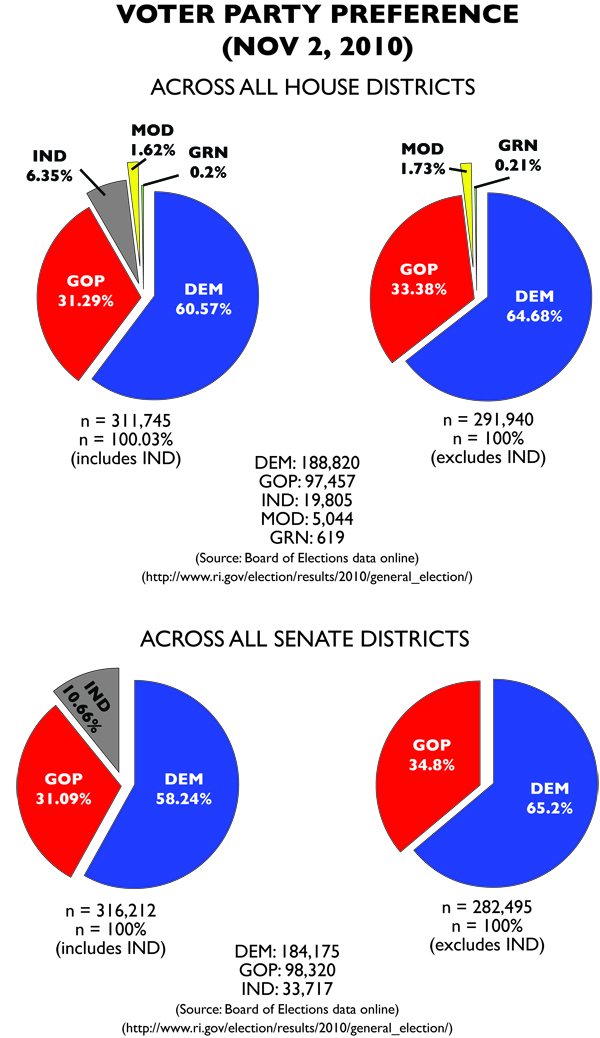
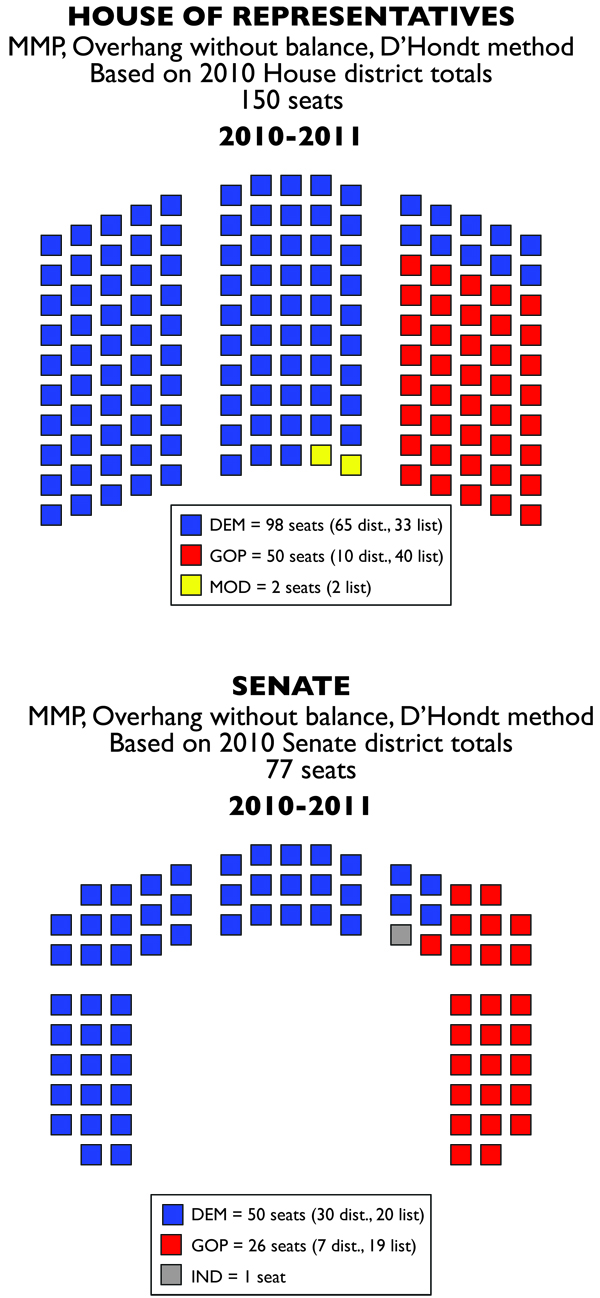
The key issue that would effect apportionment of the General Assembly were the Moderate candidates for the House. While they captured only 1.62% of the vote for House candidates, this meant they had enough to gain two seats in that chamber from their list. For first time possibly since the 1850s, a party other than the Democrats or Republicans had access to the most powerful part of Rhode Island government. Democrats also lost their veto-proof supermajority in both chambers.
Those gains came at the expense of Democrats, who lost 10 seats, with two going to the moderates, and eight going to the Republicans. Republicans managed to gain three seats from the districts as well.
In the Senate, Democrats lost six seats to the Republicans, four of which were from districts. Observers attributed the success to an abundance of general election races in the districts, though noted that much of those contests were due to independent candidates.
Implications
The 2010 election is the most interesting to me (after 1996’s Year of the Cool Moose), and it’s one I’ll return to later, but mainly because it features two statewide races with a third party candidate in it. The other thing is the nature of the Republican gains.
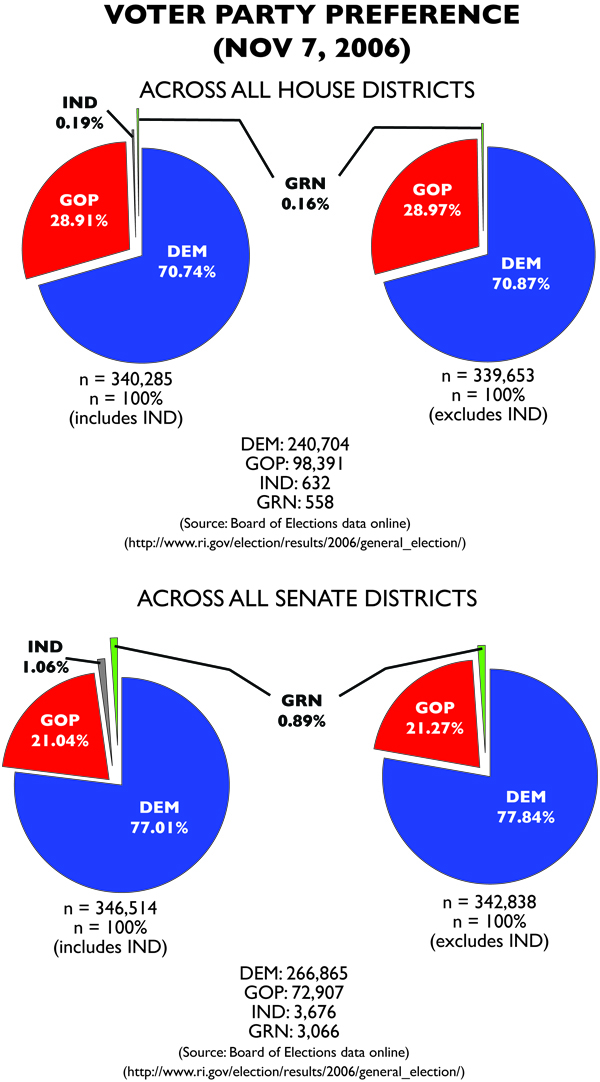
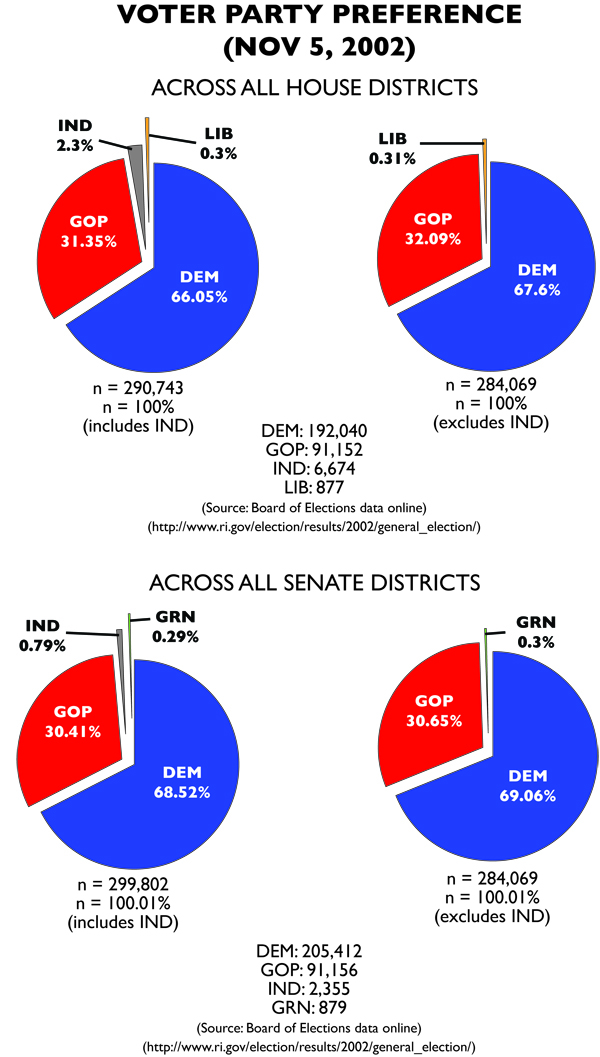
Even in real life, Republicans managed to increase their seats by 100% in the Senate and 50% in the House. The gains are less stunning in MMP, but still significant. And the primary reason wasn’t GOP motivation. Take the 2004 and 2006 elections for Democrats. Democrats won in 2006 (in the MMP version of events) due to a combination of Democratic fervor and Republican apathy.
For Republicans in 2010, their gains were almost completely due to Democratic apathy. While collectively, Republicans shed around 3000-10,000 votes, Democrats collectively lost over 90,000. These missing Democratic voters are what give the Republican Party gains, and why in the MMP version, the Moderates are able to enter the House. The Tea Party is really overblown in RI, because 2010 isn’t an election where the right wing rises up, it’s one where the left wing stays home.
The other thing to consider is that 2010 is the election in which the fewest candidates are without a challenger in the general election. It’s stating the obvious, but it’s impossible to beat an incumbent when no one runs against them.
2010 also lends credence to the idea that the way towards a healthy opposition to the Democratic Party in Rhode Island is not from the right as the Republicans and Moderates are trying, but rather from the left. A coordinated statewide campaign that effectively played on the disappointment many Democratic voters have had with the spinelessness of Democratic politicians could reap unexpectedly large dividends.
Alternatively, if Republicans wanted to win, they actually might benefit from a campaign that preyed on this disappointment to drive down Democratic turnout.
This is Part 8 of the MMP RI series, which posits what Rhode Island’s political landscape would look like if we had switched to a mixed-member proportional representation (MMP) system in 2002. Part 7 (the Election of 2008) is available here. Part 9 is a look at the Election of 2012.