The Environmental Justice League of Rhode Island (EJLRI) has created a brilliant position paper, “National Grid’s Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Liquefaction Facility: Toxic Hazards in the Port Providence: Proposals for a Just Transition” that eviscerates National Grid‘s plans to build a new liquefaction facility for fracked LNG at Fields Point in South Providence. Over the next few days RI Future will be presenting the EJLRI’s position paper in its entirety.
Environmental Racism
Beyond the potential disaster scenarios described in the previous section, there are many ongoing disasters that daily impact the front-line communities living next to Port of Providence. Business as usual under the current economic system is a state of disaster for marginalized communities, with concentrated poverty, mass incarceration, substandard housing conditions, and health disparities.
Environmental racism t?akes many forms, but is simply defined as the concentration of environmentally hazardous conditions in communities of color. A legal definition states:
“Environmental racism refers to intentional or unintentional targeting of minority communities or the exclusion of minority groups from public and private boards, commissions, and regulatory bodies. It is the racial discrimination in the enactment or enforcement of any policy, practice, or regulation that negatively affects the environment of low income and/or racially homogeneous communities at a disparate rate than affluent communities.”
The Supreme Court’s recent decision upheld the Federal Housing Act’s assertion that racism in housing policy does not need to be individually intentional if it can be shown as a systemic outcome of racial disparities.
Similarly, environmental racism is evidence as the result of sets of institutional policies and practices, regardless of whether the intent to discriminate is apparent. As described by Charles Ellison in an article titled Racism in the Air You Breathe, “?w?here you live—down to your exact zip code—can determine how fast you get sick and how soon you die.”? The following section will take a detailed look at the front-line communities of Southside (upper and lower South Providence) and Washington Park, which are right next to the Port of Providence.
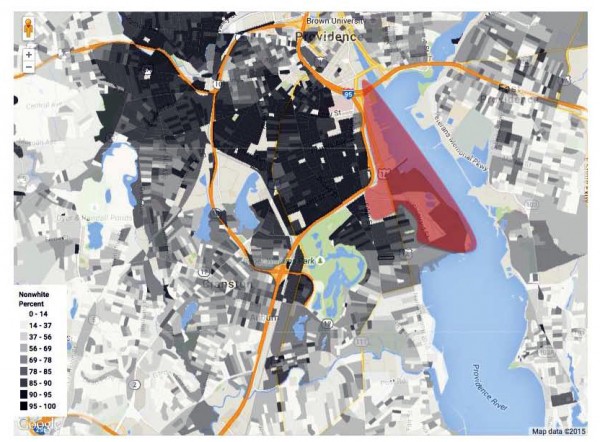
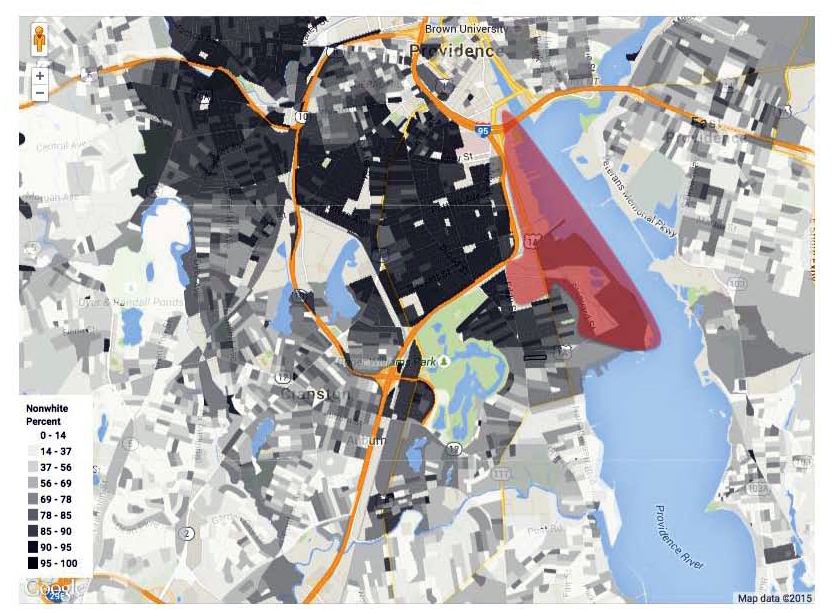
Demographics and the Waterfront?
This map shows the “percentage nonwhite” (based on 2010 census data) in a block by block geography. The approximate area of the industrial Port of Providence is highlighted in red. The line between Providence and Cranston (south of Fields Point and Roger Williams Park) shows a dramatic shift in demographics from people of color to predominately white.
The front-line communities adjacent to the Port of Providence are a corporate sacrifice zone; areas of concentrated poverty and marginalization where polluting industries are allowed to be sited and conduct hazardous operations with little regard for health or environmental impacts on the neighborhoods. This comparison of waterfront areas paints a clear picture of apartheid and de facto environmental racism. Downtown, Fox Point, and East Side / Blackstone neighborhoods in Providence, as well as Pawtuxet Village in Cranston and along the East Bay Bike Path in East Providence all have beautiful waterfront access with parks, biking, yachts, boating, sport fields, and festivals in relatively affluent and predominately white neighborhoods. Meanwhile South Providence, with concentrated poverty and communities of color, has little to no waterfront access in an area zoned for heavy industrial use with multiple polluting and hazardous facilities.
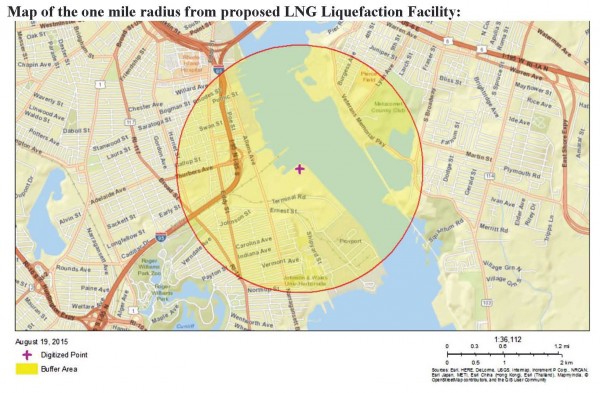
EPA Toxic Release Inventory?
This EPA database catalogues releases of toxic chemicals. All 11 polluters listed for City of Providence are included in zip code 02905, which contains a greater number of polluting facilities than any other city or town in Providence County. All 11 of the polluters listed are within the one mile radius of the proposed Liquefaction Facility, both within the industrial area in the Port of Providence and but also in the neighborhood area between Eddy St. and Allens Ave in Washington Park.
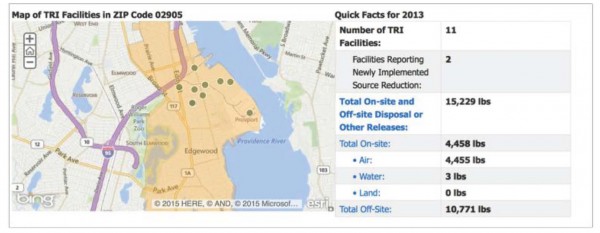
According to EPA the industry that contributes most to onsite toxic releases in the 02905 zip code are Petroleum Bulk Terminals. The TRI facilities listed include many of the risks described in the previous section, such the Motiva fuel terminal (Petroleum Bulk Terminals) and Univar USA Inc (Chemical Wholesalers), as well as facilities located even closer within residential communities: Monarch Metal Finishing Co (Fabricated Metals), SafetyKleen Systems, Inc (Hazardous Waste/Solvent Recovery) and Mahr Federal, Inc. (Computers/Electronics Products).
Schools at Risk
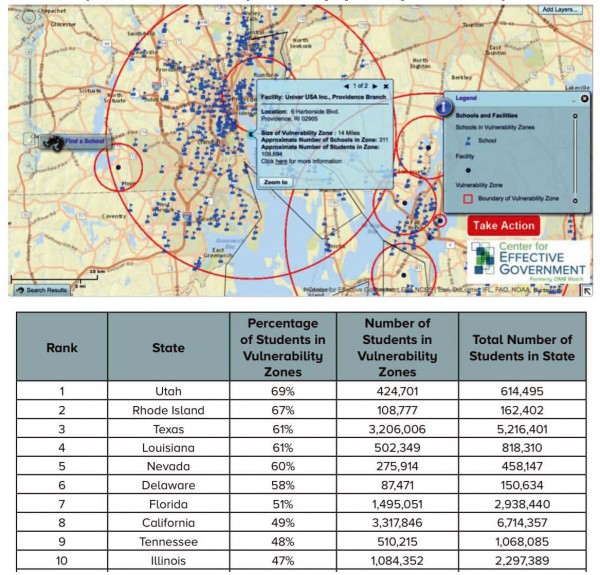
A?s described earlier, the Univar chemical facility has a 14 mile hazard radius, pictured below as the large red circle. There are 311 schools within this zone, which are attended by approximately 110,000 children. The table below shows the national rankings of the percent of children within vulnerability zones. RI’s high ranking is due almost entirely to the Univar facility in Port of Providence, adjacent to the proposed Liquefaction Facility.
EPA’s EJ SCREEN Tool
This new interactive mapping tool is a way to analyze the intersection of demographic risk profiles alongside environmental indicators such as air quality (particulate matter and ozone levels), lead paint, and proximity to traffic or facilities that require a chemical risk management plan, that store and process toxic materials, or that are water discharge polluters. The results can be mapped out and compared to the rest of the state, the rest of the EPA region, or nationally. In all of the following maps, the national percentile is displayed with the 95th100th percentile in red and 90th95th percentile in orange.
Proximity to Facilities Requiring a Chemical Risk Management Plan
The following map shows the Greater Providence area and highlights the areas that have close proximity to a large chemical facilities that require having a chemical Risk Management Plan (RMP). The area adjacent to the port is highlighted in red, meaning that it is in the 95th – 99th percentile nationwide in a combined measure of chemical risk proximity and demographic risk.
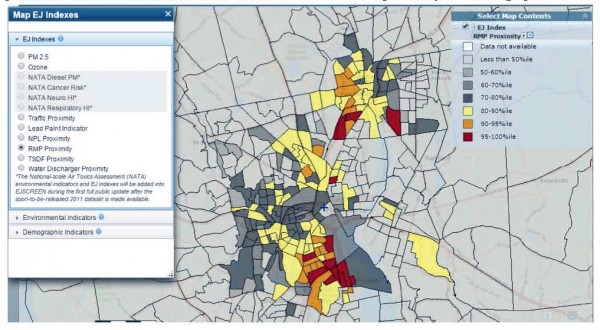
The one mile radius around the proposed Liquefaction Facility ranks in the 97th percentile for the state, the 98th percentile for EPA Region 1 (New England), and 95th percentile nationally. This is an Environmental Justice community that is at high risk for exposure in a chemical incident.
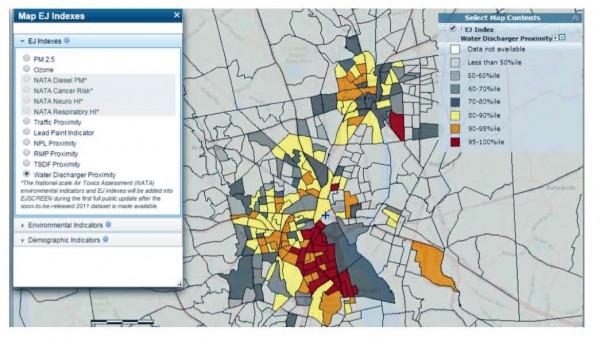
Proximity to Water Discharger Facility
The following map for the combined EJ indicator for proximity to Major Direct Water Discharger Facilities and demographic risk. Again, the areas in Providence closest to the port are in the highest percentiles nationwide. In state, regional, and national comparisons, the one mile radius from the proposed facility is in the 97th percentile for this risk factor.
Traffic Proximity
The following map shows the EJ SCREEN risk status for Traffic Proximity and Volume. The one mile buffer from the site is in the 96th percentile for both state and national comparisons, and in the 98th percentile compared to the rest of EPA Region 1.

Traffic proximity and volume is an issue that requires careful attention for the proposed liquefaction facility. The I95 corridor is a major interstate roadway with heavy vehicle traffic. The Thurbers Ave exit, Eddy St. exit, and residential streets along Eddy St. and Allens Ave. carry most traffic in and out of the Port of Providence, and are located in some of the largest asthma hot spots in the state. This asthma hot spot has a high concentration of people with asthma (impacting Black and Latino families most) and some of the highest rates of emergency room visits and hospitalizations due to asthma. Air pollution in the form of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM), ultra-fine particles, and black carbon are connected with heavy vehicle traffic and especially truck traffic. These air pollutants are known asthma triggers and are also linked to other respiratory health issues, certain cancers, and developmental disabilities. This is an existing burden that severely impacts Southside and Washington Park neighborhoods. The construction and operation of the liquefaction facility will be additional cumulative impacts in an area that is already overburdened. The proposed export of LNG via tanker trucks is a large concern: why should these communities now bear the burden of supplying the rest of RI and MA with LNG? National Grid says that there won’t be a net change in truck traffic, with 16 tankers per day currently delivering LNG and an estimated 16 tankers per day exporting LNG once the facility is built. However, there are no binding guarantees this wouldn’t increase later. National Grid’s partners in Access Northeast are proposing major new LNG storage tanks near New Bedford, if these tanks are built would they be supplied with LNG from Fields Point? FERC should analyze the production capacity of this facility and determine if the supply produced would require additional tanker traffic to distribute. In either case, the two years of construction will have a significant impact on additional traffic in the community.
Toxic Storage and Discharge Facilities
Toxic materials are a major issue in these neighborhoods, and are some of the highest ranking EJ Indexes placing all of South Providence and West End above the 95th percentile.
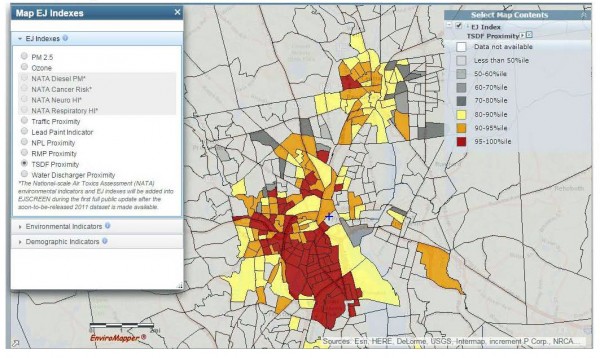
For proximity to Toxic Storage and Disposal Facilities, communities in the one mile radius surrounding the proposed facility are in the 98th percentile for the state and the 99th percentile for EPA Region 1 and National comparisons.
Environmental Justice: working towards equitable healthy environments
In simplistic terms, environmental justice means guaranteeing equitable access for all people to have healthy environments where they live, work, play and pray. For a more detailed description of environmental justice, please read the EJ Principles. The environmental justice movement has exposed the reality of the extent to which this equitable world does not exist. Because of ongoing legacies of racism, economic inequality, segregation, redlining, and other systemic injustices, someone’s zip code is the greatest factor in their health and life expectancy. Unfortunately, the front-line communities next to the Port of Providence, which are densely populated and filled with schools, day cares, home, and healthcare facilities, are a prime example of an area suffering from a concentration of pollution and a lack of environmental benefits such as parks, healthy food, and safe recreational areas. Many of the numerous schools in the community are crumbling and don’t have funding to deal with issues such asbestos, lead paint, mold, and poor indoor air quality. At home, many residents are faced with substandard housing quality. The high percentage of older homes means that many are energy inefficient, have lead paint, and are likely to have mold, mildew, and other air quality issues. Homeowners in the community were and continue to be hard hit by the foreclosure crisis, and the high percentage of rental apartments means that many residents are dependent on landlords to improve housing quality and make home more energy efficient. For homes that aren’t owner occupied, there is no financial incentive for the owner to make these upgrades, and the tenants are the ones who suffer from high energy costs and negative health impacts.
See also:
? Flawed Proposal: Background info on National Grid’s unnecessary project
? Potential Disasters: dangerous facility in a high risk area
? Environmental Racism: ongoing and underlying environmental justice issues
? Climate Change: it causes climate change and is at risk from climate impacts
? Public Health: health disparities and impacts on health care institutions
? Economic Inequality: high cost project that will cause economic damage
? Alternatives and Solutions: Strategies for Climate Justice & a Just Transition

Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387
Deprecated: Function get_magic_quotes_gpc() is deprecated in /hermes/bosnacweb08/bosnacweb08bf/b1577/ipg.rifuturecom/RIFutureNew/wp-includes/formatting.php on line 4387