 Rhode Island-based Textron is one of four private-companies on earth, and the last North American producer, to manufacture what is quickly becoming one of the world’s most controversial weapons of war: cluster bombs.
Rhode Island-based Textron is one of four private-companies on earth, and the last North American producer, to manufacture what is quickly becoming one of the world’s most controversial weapons of war: cluster bombs.
“The cluster munition industry is gone because many nations have banned the weapon,” said Mark Hiznay, a senior arms researcher for Human Rights Watch.
“Most foreign producers are state-owned industries,” he said, such as China and Russia. In addition to Textron he knows of only three other privately-held companies in the world that still make cluster bombs, two are in South Korea and one is in Singapore.
Human Rights Watch recently released a report criticizing the failure rate of Textron-made cluster bombs and accused Saudi Arabian-led forces in Yemen of using them dangerously close to civilians.
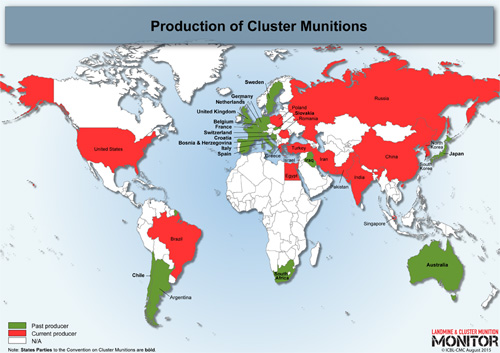
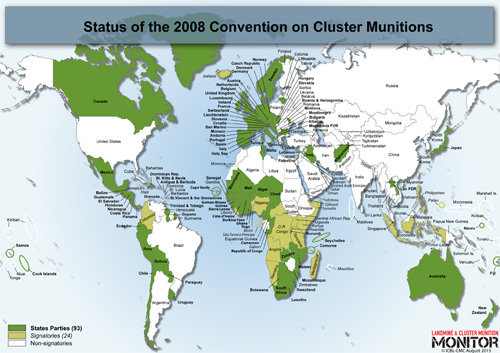 At one time 34 different nations made cluster bombs but now only 16 still do, or reserve the right to, according to the Cluster Munition Monitor, an annual report of the sale, use of and efforts to ban cluster bombs. 119 countries have banned them. Canada, Germany, Italy, Japan and England, among others, have already destroyed their entire stockpiles, Hiznay said.
At one time 34 different nations made cluster bombs but now only 16 still do, or reserve the right to, according to the Cluster Munition Monitor, an annual report of the sale, use of and efforts to ban cluster bombs. 119 countries have banned them. Canada, Germany, Italy, Japan and England, among others, have already destroyed their entire stockpiles, Hiznay said.
The United States, on the other hand, has not signed the 2008 Convention on Cluster Bombs treaty. In 2003, the US military used Textron-made cluster bombs against Iraqi tanks as it advanced on Kirkuk.
Both of Rhode Island’s senators say they see the need to curtail the use of cluster bombs.
“Senator Reed has supported efforts to limit the sale and transfer of cluster munitions and to ensure the use of more precise technologies to protect civilians,” said his spokesman Chip Unruh.
Senator Sheldon Whitehouse is a co-signer of the Cluster Munitions Civilian Protection Act. “Cluster bombs can take a terrible and lasting toll on civilians, which is why I’ve cosponsored legislation to restrict their use,” he told RI Future. “I hope the Senate will take action on this bill to help protect innocent civilians from these dangerous weapons of war.”
The House-version of this bill is sponsored by Massachusetts Congressman Jim McGovern, who represents the Worcester area. Congressmen David Cicilline and Jim Langevin could not be reached for comment.
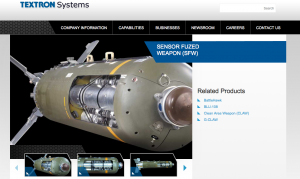 The Textron-made bomb – the CBU-105 Sensor Fuzed Weapon – is at the center of a new Human Rights Watch report that indicates the weapon malfunctions more than 1 percent of the time, a violation of US export law, and accuses the Saudi Arabian-led forces in Yemen of using the weapon dangerously close to civilian populations which has resulted in several documented injuries.
The Textron-made bomb – the CBU-105 Sensor Fuzed Weapon – is at the center of a new Human Rights Watch report that indicates the weapon malfunctions more than 1 percent of the time, a violation of US export law, and accuses the Saudi Arabian-led forces in Yemen of using the weapon dangerously close to civilian populations which has resulted in several documented injuries.
“It’s puzzling to us that Textron is marketing this as a reliable weapon,” Hiznay said. “We’re not sure if it’s Textron’s problem or the Saudis’ problem, but we’ve had the US Air Force use them in Iraq and produce duds and now we have Saudi forces using them and producing duds in Yemen.”
US export law requires cluster bombs sold to foreign countries to malfunction less than 1 percent of the time, a success rate Human Rights Watch says the Textron-made bomb has not achieved. A 2008 Department of Defense Directive, the current prevailing US policy on the use of cluster bombs, requires the US military to only use cluster bombs with similar success rates.
“Most of the SFW’s have been sold to the US Air Force,” said Textron spokesman David Sylvestre in an email. “Comparatively few have been sold to US allies.” He declined further comment about the sale of weapons saying, “Much of the data about what we sell to a particular military customer may be considered protected or classified info by the US government or the customer.”
According to a 2011 Department of Defense news release, Textron was contacted to sell 404 cluster bombs to Saudi Arabia for $355 million. In 2012, Textron was contracted to sell 325 cluster bombs to South Korea for $325 million. The US last put aside funds to buy cluster bombs from Textron in 2007, said Hiznay, but didn’t make the buy after the weapons malfunctioned more than 1 percent of the time.
“We believe that SFW is truly the best area attack weapon in the world,” said Ellen Lord, senior vice president and general manager of Textron Defense Systems. “Through a process of rigorous research, testing and analysis, we have created a weapon that is reliable, safe and meets current clean battlefield standards.”




 As it turns out, Monty Python was right: Finland isn’t just a
As it turns out, Monty Python was right: Finland isn’t just a