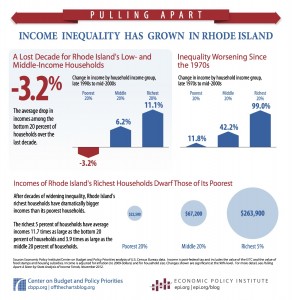
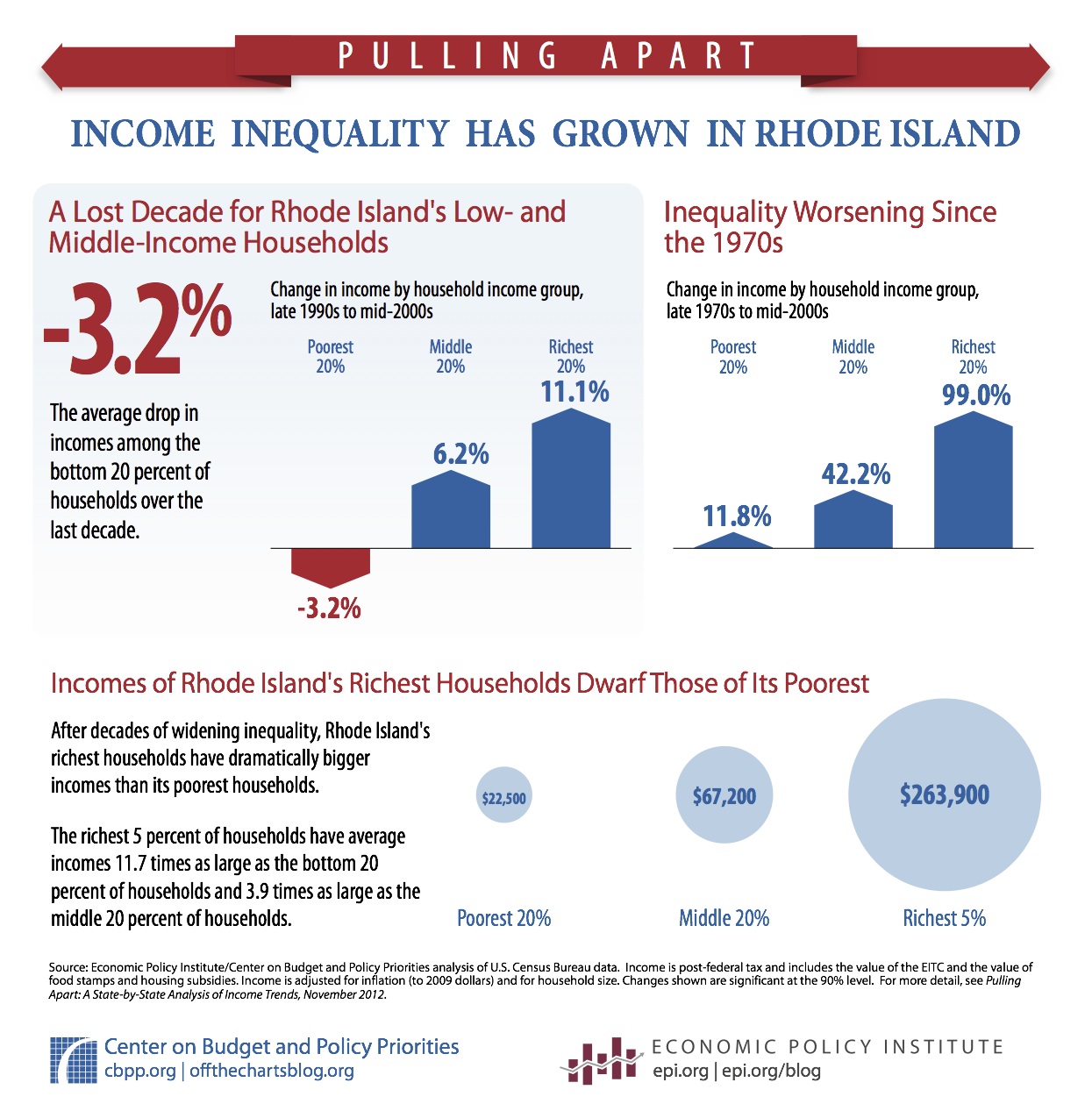
In my last post, I talked about Clarence Thomas and his truly remarkable rise to a position that his father could never, ever have achieved. Indeed, even a slightly older Mr. Thomas would probably not been able to attain such a truly lofty height.
In my last post, I talked about Clarence Thomas and his truly remarkable rise to a position that his father could never, ever have achieved. Indeed, even a slightly older Mr. Thomas would probably not been able to attain such a truly lofty height.
This all sort of gets to the idea of social mobility. If someone were born into conditions like those into which Mr. Thomas was born, how likely is it for that person to improve his level of economic security? Or, how likely is it for someone born into the upper echelons, such as Mr. Thomas’ children (does he have any?) to fall out of the exalted perch onto which she was born?
America has long perpetuated the ideal that everyone can improve their status. This is still true. It is still possible. But how likely is it? Or, how probable is it? And here, I use ‘probable’ in the technical sense of “Probability and Statistics”, the name of a book on my shelf. “Possible” and “Probable” are two very different words, with enormously different implications. The right wing continues to flog the notion of possibility. Sure, it’s possible. It’s possible that I can throw a ball through a solid wall, too. Or that all the air molecules in a room will suddenly rush into one corner and leave the rest of the room airless. But are these events likely to happen? No. According to the technical definition, that means, that they have an extremely low probability of occurring. Could a high school basketball team beat the Celtics? I suppose it’s possible. But the probability of this occurring is darn close to zero. It may not be exactly zero, but it’s probably (!) close enough to be considered zero in any real-world scenario.
Let’s set this up. Suppose you have been put into a situation in which you must choose one of two balls. One is yellow; the other is green. If you choose the correct ball, you will be given $100 million. If you choose the wrong one, you will have to spend the rest of your days working at a minimum wage job. Of course, you don’t know which ball gives the desired outcome, so you have to guess. And hope. And, as any fool knows, you have a 50/50 chance of getting it right. And an equal chance of getting it wrong. In other words, it’s a coin flip.
But let’s say we change the scenario, and introduce a blue ball. But even given the extra ball, there is still only one ‘correct’ choice. One ball will get you the $100M; either of the other two will get you consigned to the minimum wage. What has happened to your chance of success? It has been diminished. It has gone from 1 in 2, to 1 in 3. That is, rather than a 50% likelihood of success, you have a 33% chance.
For the next iteration, we’re back to two colors, red and green. The red ball gets you the $100M; the green results in the minimum wage job. But you have to pick either of the two balls out of a basket in absolute darkness, so you can’t see which ball is which. We’re back to 50/50. But let’s start adding green balls. If we add two more green balls, for a total of three green, one red, your chance of success has been cut in half. It’s now 1 in 4, or a 25% chance of success. Starting to look grim, isn’t it? Now let’s bring the total of green balls up to ten. This is a 1 in 11 chance, and suddenly your chances of success drop below 10%.
This is what tax cuts, cutbacks in social spending, cuts in education have been doing: they have been adding green balls into the system. At least, they’ve been adding green balls into the basket from which those on the lower end of the scale have to choose. At the same time, these policy choices—tax cuts, cuts in social spending, cuts to education—have been adding red balls into the basket from which those born into the upper echelon get to choose. In other words, we’ve been increasing the odds against success for those in the bottom half, while increasing them for those at the top. Put another way, we’ve been rigging the game in favor of those at the top. How would you feel about entering the game with the odds of success sitting at 11 to 1 against you? Would you want to take a chance on winning the $100M if there were a 9o% chance of being consigned to the ranks of minimum wage workers? Kinda stinks, doesn’t it?
This is what I meant in my previous post about my good fortune. I got to pick from a basket that was probably 75% red (good) balls. Yes, I could have failed, made a lot of bad choices, and ended up dropping. But the game was rigged in my favor from the start. Yes, I had to work for what I got, but that does not change the fact that I had an enormous head start over a lot of people.
And that, I think, is the clearest difference between a liberal and a conservative. A liberal recognizes—or never forgets—where she or he started. A liberal is aware that there were, there are always extenuating circumstances. Had Clarence Thomas worked twice as hard, but lived in the wrong place or time, all his effort may have been in vain. A conservative, from what I see, becomes convinced that they made it solely on their own merits. They fail to contextualize their success. They remember the work they put in to getting where they are, and nothing else. Yes, this is not the whole story of the differences between the two, but I think that it may be the single key difference. Clarence Thomas, or Rush Limbaugh, or—the golden example—George W Bush are all convinced that they did it on their own. No one helped them. They don’t think that the stable family environment, or the genes or temperament that put the grit into their belly to succeed was an advantage that, perhaps, other people don’t have. They don’t see that being in a semi-decent school with semi-decent parents who instill values gives them a big leg up on a lot of other people. They forget that they happened to be born at a good time, or a good place.
So conservatives don’t see why other people might need help. Perhaps growing up they did not have the advantage of government assistance (but they did; they just fail to recognize this, or to acknowledge this), so why should other people get this help? So we continue with the aforementioned policy choices—tax cuts, cuts in social spending, cuts to education— and what we’re doing is increasing the number of people who have to choose from the basket of mostly green (bad) balls. Each cut to Head Start, or SNAP, or job training, or education, we’re both adding to the number of green balls and increasing the number of people choosing from this basket. In other words, we’re stacking the deck against them. Such behavior would get you shot in a lot of gambling establishments. Ask Wild Bill Hickok.
If you don’t believe me, here’s some evidence.
http://www.pewtrusts.org/uploadedFiles/wwwpewtrustsorg/Reports/Economic_Mobility/PEW_Upward%20EM%2014.pdf
Take a look at the chart on page 10 of the report at the link. For someone born into the bottom income quintile, there is more than a 33% chance that they will end up there. For someone born into the top quintile, the odds are over 37% in favor of them remaining. But it’s worse than that. There is a cumulative probability of 60 percent that someone born in the bottom quintile will stay in one of the bottom two quintiles. That is, they will never be above what the lowest 40% of the country makes. That is, they only have a 40% chance of making it to middle class.
BUT: for each percentage point you move up in the scale, your chances of remaining in the top levels goes up. That is, someone born in the 95th percentile, their chances of staying there are about 75%.
As for where the most people make it, or remain stuck where they are, check out the second link.
http://www.equality-of-opportunity.org/
What you find is that the places with single-digit movement from the bottom to the top are largely in the South. You know, the area of the country where low taxes, low union density and small-but-business-friendly government is attracting lots of Good Jobs. Just gobs and oodles of them! Charlotte, North Carolina is a great example of how this works. Remember, MetLife was planning to move several hundred jobs from RI, and a thousand (or more) from the Northeast to Charlotte, that land of opportunity. See! Charlotte attracts Good Jobs! But, per the second link, of the top 50 metropolitan areas in the US, Charlotte is #49 in inter-generational upward mobility. There, only 4% of those born in the bottom quintile can be reasonably expected to reach the top quintile. And note, that means the 81st percentile. Admission to this is a salary of about $78k per year. We’re not talking about top-flight surgeons, or anything such. We’re talking a solid job, something around what a teacher with ten years experience makes here. So the chance of someone being born into the bottom quintile of ending up with a job with a teacher’s salary is less than 5%, or 1 chance in 20. How would you like to pick from that basket?
As for the idea of talent, well, it ain’t what it used to be. An average student born into a family in the top quintile is several times more likely to graduate college than a bright student born into the bottom three quintiles. What this means is that the uninspired student from wealth is picking from a basket with lots of red (good) balls in it. And even if someone from the bottom 40% does beat the odds and finish college, that’s not the guarantee of success it once was. Average wages for college grads have been falling over the past 10 years, so I don’t want any nonsense about how all people have to do is pull themselves up by their bootstraps and work their way through college, blah, blah, blah.
Is this the kind of country we want? Where most people are pretty much destined to fail?