My colleague Steve Ahlquist previously posted a great story covering the two meetings on July 27 about the proposed construction of the taxpayer-subsidized stadium. One point that was made at the Providence meeting, worth expanding on here, is the issue of the construction trade unions, which have endorsed this project. This piece will make an effort to appeal to both the general membership and leadership of these unions, who will prove to be some of the most important allies in this struggle and, on the other hand, will perhaps be the make-or-break of this deal.
It is important to empathize with the membership, they are facing a massive drop in employment and job sites, with a huge percentage of the rank-and-file out of work. This project would create jobs for a large swathe of their members, something I do not begrudge them for.
But this is a decision I do not think they have properly contemplated. First, while the governor has previously eluded to a hiring push that would target minority workers, the current contractor participating in this project, Gilbane, has one of the worst records of minority hiring in the nation. That is an important issue to discuss because the disenfranchisement of minority workers is a vital one.
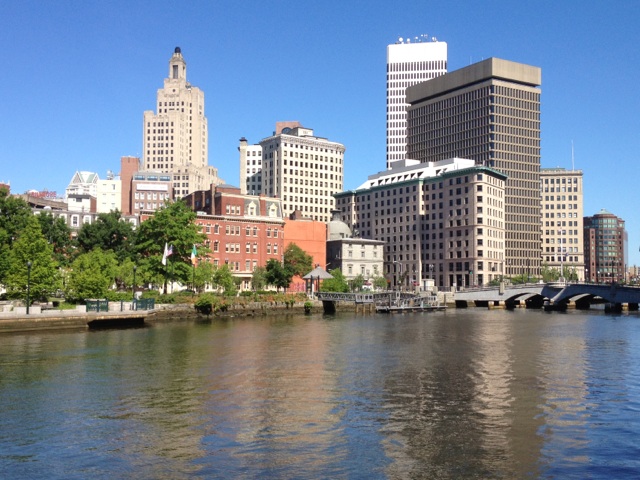
Second, and perhaps more importantly, this stadium could generate short-term gains on one project but may in fact kill development in the I-195 land in the near future. As Kate Bramson reported on May 2, any and all further construction hinges on a super-permit that would install a stormwater mitigation mechanism at the proposed open park. Bramson wrote in that piece:
The master permit hinges on a plan to use parkland within the 195 district for stormwater mitigation. Builders are required to treat a percentage of stormwater on parcels they develop. However, if they can’t meet the entire stormwater requirement on a parcel, the master permit allows them to gain credit from the parkland’s treatment of stormwater.
Given the tides and ebbs of Rhode Island politics, this could end up killing future development on the I-195 corridor for up to five years. And on top of that, recall that the federal government also will need to be involved, prolonging the wait. That of course translates out to a much greater amount of time for unemployed union members to remain so. Between an extended waiting period and a traffic-clogging stadium, potential developers in the bio-med and education sectors might take their business elsewhere, keeping that land vacant for a very long time.
Bucking the trend and opposing an endorsement that has already been made by the union is always a tremendously problematic issue, no doubt. It takes courage, gumption, and being versed in the relevant documentary records so to make a cogent case. I would refer interested parties especially to this slideshow produced already by the I-195 Commission, an outline of proposed development by landscape architects that every taxpayer in the state already funded. Just to re-iterate, the state has already paid three times for this land. First, we paid for the de-comissioning and demolition of the old I-195 highway. Second, we paid to have it zoned and developed by the federal government. Third, we paid for the aforementioned landscape architects and other planners to work out the schematics of the park.
If this ballpark scheme goes through, it will cost taxpayers another three times. First they will need to pay for the stadium’s construction. Second they will pay to re-design the sewer and highway system to accommodate the stadium. Third we need to re-develop another parcel of land as a park should the government refuse to accept the idea of a smaller park on the grounds of the stadium.
There is simply too much risk as opposed to reward in this idea and organized labor should rethink their position, not so to undermine their standing but to promote and improve their reputation. This week Boston Mayor Martin Walsh rejected the move to finance the 2024 Olympics with Beantown tax monies, causing their bid for the Games to be voided. That move has probably bought Walsh another term in office and could very well give him a future bid for higher office. The unions in Rhode Island would be wise to take such logic into consideration. To be clear, I am no opponent of labor unions, I am a member of one and was an eyewitness to the Illinois Caterpillar strike in the 1990’s. But this project, should it come to pass due to labor’s support, will be seen by many as a black mark on its record and will be fantastic fare for union busters on both sides of the aisle.